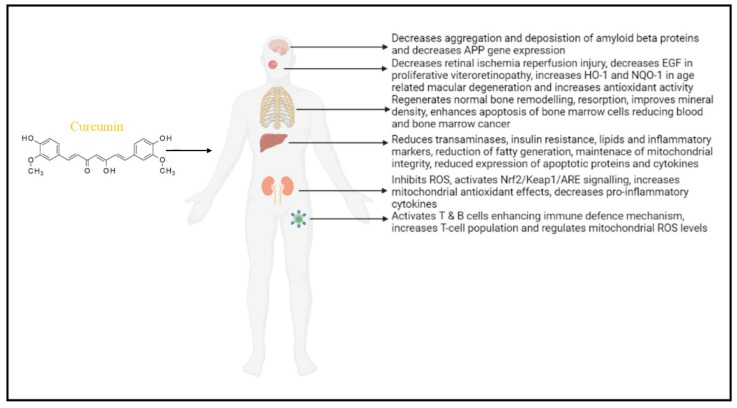
Figure 2.
Role of curcumin in reducing mitochondrial dysfunction in various organs: in the brain—Alzheimer’s disease; eye—retinal infection; skeletal system; liver function; kidney disease, and lymphocyte regulation. Curcumin mainly regulates ROS levels and maintains the antioxidant system for proper regulation of mitochondrial function. (APP—amyloid precursor protein; EGF—epidermal growth factor; HO-1—Heme oxygenase 1; NQO1—NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1; Nrf2—nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Keap1—Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; ARE—antioxidant response element.).