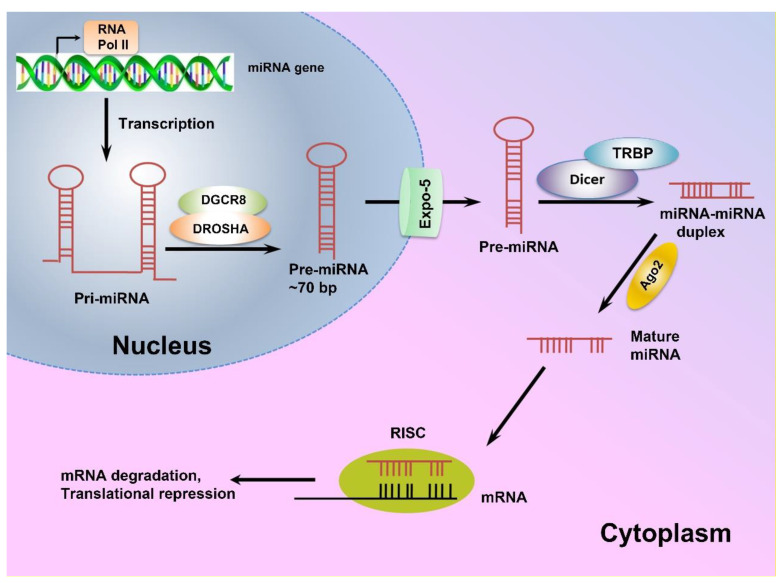
Figure 1.
The schematic view of miRNA biogenesis. MicroRNAs are mainly transcribed by RNA polymerase II as long pri-miRNAs, which are then processed in the nucleus by Drosha endonuclease and its cofactor DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region 8 (DGCR8). Next, exportin-5 transports the resulting pre-miRNA to the cytoplasm where a complex of Dicer enzyme and TAR RNA binding protein (TRBP) creates a double-stranded miRNA which is unwound to a mature single-stranded miRNA. Finally, the single-stranded miRNA is assembled into a miRNA-induced silencing effector complex (RISC), leading to complementary mRNA sequence and regulating gene expression post-translationally [45,49].