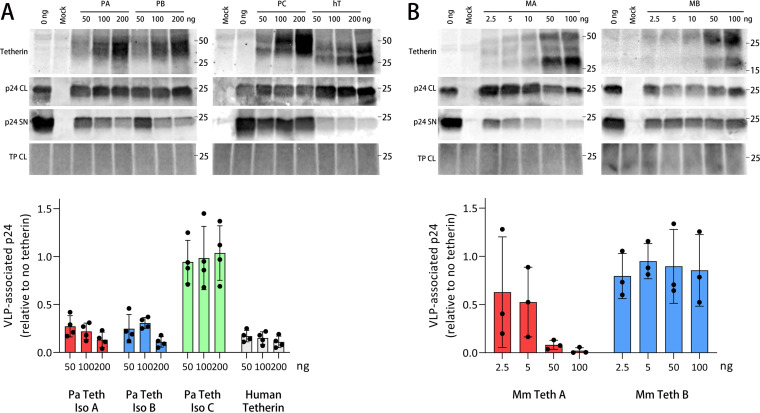
FIG 12.
Bat tetherin restricts the release of HIV-1 virus-like particles (VLPs). (A) P. alecto tetherin isoforms A (PA), B (PB), C (PC), or human tetherin, co-transfected with a HIVΔVpu construct. (B) M. macropus tetherin A (MA) and tetherin B (MB) co-transfected with a HIVΔVpu construct. Mammalian HEK293T cells were co-transfected with 200 ng of the HIVΔVpu plasmid expression construct encoding the HIV Gag-Pol polyprotein, which generates HIV-1 VLPs that do not include the tetherin antagonist Vpu, and 0 to 200 ng of the tetherin plasmid expression vector. VLPs were harvested at 48 h and concentrated by ultracentrifugation using a sucrose cushion. VLP and cell lysates (not deglycosylated) were subjected to reducing SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. HIV-1 VLPs were detected with a mouse anti-p24 primary antibody and goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 680 fluorophore-conjugated fluorescent secondary antibody. Tetherin was detected with a rabbit anti-HA primary antibody and goat anti-rabbit Alexa-Fluor 800 fluorophore-conjugated fluorescent secondary antibody. Representative Western blots are shown. Protein molecular weight is expressed in kDa. Total protein stain was used as a loading control. The extent of VLP restriction was quantitated by densitometric analysis of Western blots comparing the relative ratios of VLPs present in the viral lysates and cell lysates from n = 4 (P. alecto) or n = 3 (M. macropus) independent assays. Error bars represent the standard deviation. HIV-1, human immunodeficiency virus type 1; SN, cell culture supernatant; CL, cell culture lysate; TP, total protein stain.