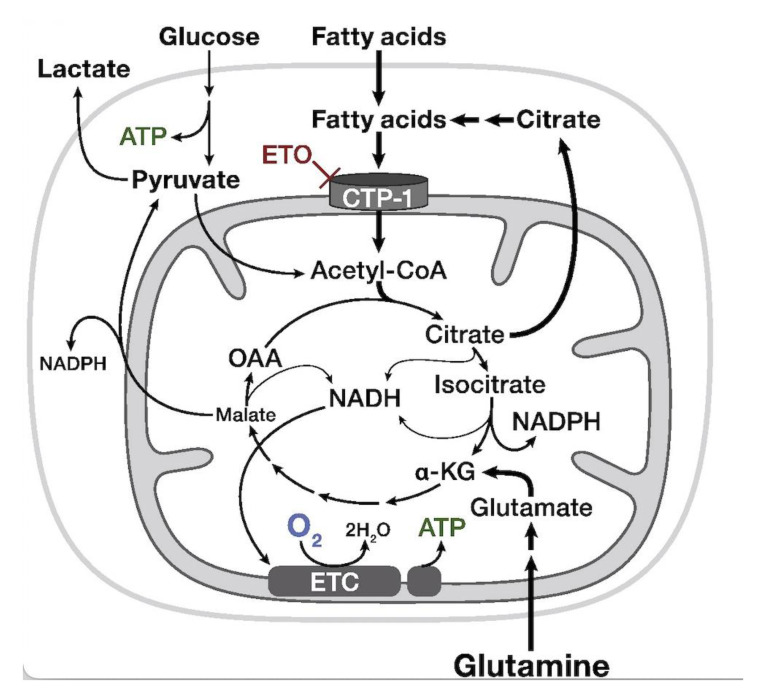
Figure 4.
Illustration of fatty acid oxidation and synthesis in mitochondria. Fatty acids enter the mitochondria for β-oxidation to Acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters the TCA cycle generating NADH. The NADH is then oxidized by the ETC, consuming oxygen or producing NADPH, as indicated. Endogenous fatty acids can be synthesized de novo from glucose or glutamine. Glucose is converted to pyruvate via a series of catabolic reactions, and the resultant pyruvate is either converted to lactate or enters the mitochondria to be converted to Acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters the TCA cycle and exits as citrate, which is then exported to cytosol for the synthesis of fatty acids. Glutamine enters the TCA cycle after conversion to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and exits as malate and citrate into the cytosol for fatty acid synthesis. ETO: etomoxir, a CPT-1a inhibitor. Reprinted with permission from [75].