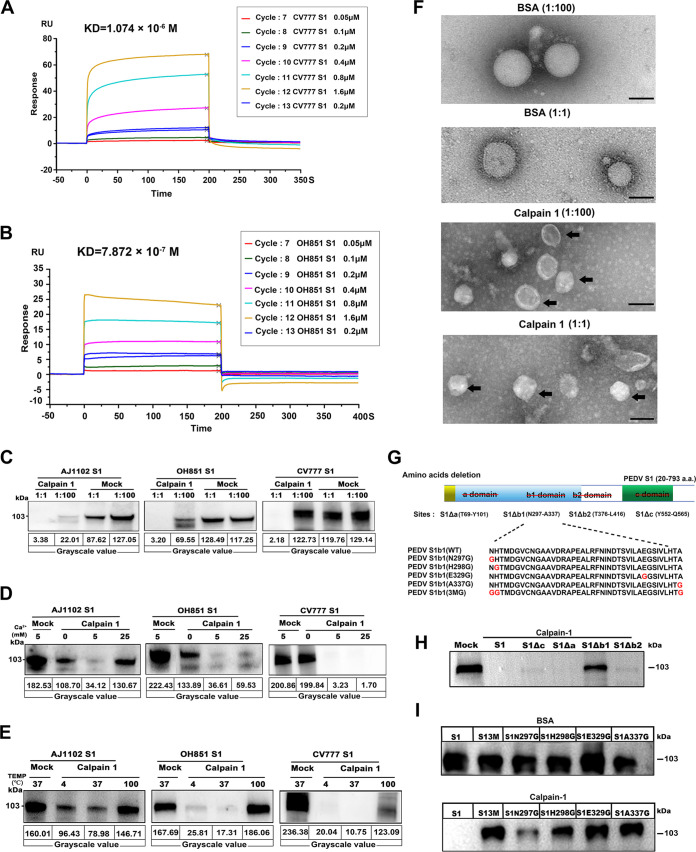
FIG 5.
Proteolytic effects of calpain-1 on S1 domain of PEDV spike protein were analyzed in vivo. (A, B) Kinetic constant analysis of the interaction of calpain-1 with S1 protein of classical (CV777) PEDV (A) or variant (OH851) PEDV (B) was determined using surface plasmon resonance assay. (C) Cleavage of S1 by calpain-1 in vitro, as detected using Western blot analysis. Purified recombinant S1 protein from classical (CV777) and variant (OH851 and AJ1102) PEDV strains were incubated with calpain-1 at a ratio of 1:1 and 1:100, respectively (37°C for 2 h; 5 mM CaCl2 included in reaction mixture). BSA was used as a negative control. (D, E) Effect of calcium concentration and incubation temperature on calpain-1 activity. (D) PEDV S1 proteins were incubated with calpain-1 at a ratio of 1:1 (37°C for 2 h), while different concentrations of calcium were added to the reaction system. (E) PEDV S1 proteins were incubated with calpain-1 at a ratio of 1:1 (5 mM CaCl2 included in reaction mixture), while the incubation temperature was set at 4, 100, or 37°C for 2 h. (F) Effect of calpain-1 on PEDV structure visualized using transmission electron microscopy. Bar = 100 nm. Black arrows indicate viral particles with envelope-anchored S protein shedding. (G) Schematic diagram of PEDV S1 protein deletion mutants and five S1 proteins with point mutations in the b1 domain. The red line crossing out letters in the upper panel indicates the deletion of different domains (a, b1, b2 and c) in PEDV S1 protein; red letters in the bottom panel represent mutation sites. (H) Proteolytic effect of calpain-1 on deletion mutants of PEDV S1 (CV777). (I) Proteolytic effect of calpain-1 on five S1 proteins with point mutations in the b domain. BSA was used as a negative control. All data are presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments; BSA, bovine serum albumin.