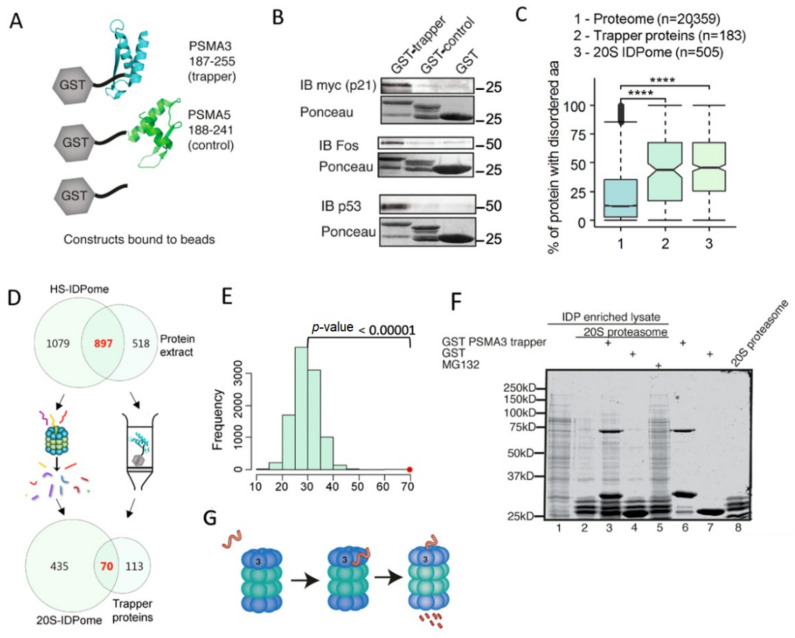
Figure 4.
Isolated PSMA3 C-terminus interacts with many intrinsically disordered proteins. (A) Illustration of constructs used and experimental strategy. (B) Purified GST, GST PSMA3 trapper and GST PSMA5 C terminus (control) bound to glutathione agarose beads were incubated with HEK293 cell lysate overexpressing 6xmyc p21 or naive HEK293 cell lysate. GST constructs and the interacting proteins were eluted with 10 mM reduced glutathione. GST constructs were visualized with Ponceau and interacting proteins; myc-p21 and endogenous c-Fos and p53 were detected by immunoblot (IB). (C) The different GST-chimeric proteins described in A were incubated with cellular extract. The bound proteins were identified by MS. One hundred fifty-seven proteins were retained on the GST–PSMA3 trapper fragment, whereas only nine were retained on the GST–PSMA5 C terminus fragment. The former group was analyzed for IDP/IDR content. The Boxplot shows the IDP/IDR content of the proteome compared to the trapped proteins by the PSMA3 C-terminal fragment and to the 20S IDPome group. **** p ≤ 0.0001 (D) Venn diagram of the proteins retained on the column containing the GST–PSMA3 trapper fragment and the 20S IDPome. (E) The expected average number of shared proteins between the two groups in Panel D was evaluated by a Z-test with the null distribution calculated by 10,000 simulations. The expected intersection number is approximately 25 proteins, whereas the observed number is 70 (red dot, p-Value < 0.00001). (F) HEK293 IDP-enriched lysate was incubated for three hours at 37 °C with purified 20S proteasome, GST–PSMA3 trapper and GST as indicated. Protocol for 20S purification was previously described [18]. Proteins were visualized with InstantBlue stain. (G) A model describing the steps of IDP recognition by the trapper and degradation by the 20S.