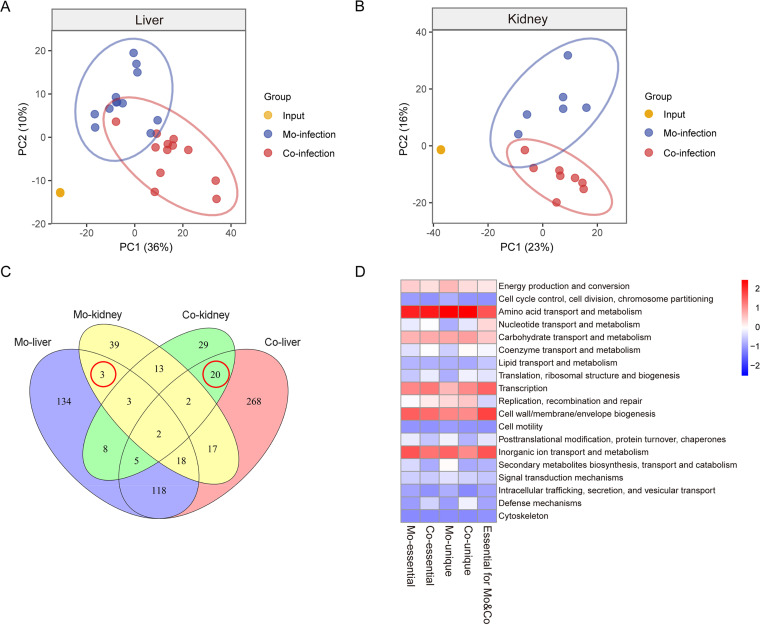
FIG 3.
Clustering and functional annotation of Tn-seq data. (A) Principal-component analysis of the normalized Tn-seq counts recovered from the liver in three conditions: input (orange, n = 4, the points are overlapped), mono-infection (blue, n = 12), and co-infection (red, n = 12). (B) Principal-component analysis of the normalized Tn-seq counts recovered from the kidney in three conditions: input (orange, n = 4, the points are overlapped), mono-infection (blue, n = 6), and co-infection (red, n = 8). (C) Venn diagram of the essential genes of S. aureus required for in vivo colonization of the liver and kidney both in mono-infection and co-infection with A. baumannii. The red circle depicts the genes essential for colonization of both the liver and kidney while also being divergently required for mono-infection or co-infection. (D) Heatmap of COG functional categories of the essential in vivo genes of S. aureus. Conserved COG functionality was assigned to both infection conditions, while differentiated requirements were observed for genes unique to mono-infection and co-infection conditions.