FIG 4.
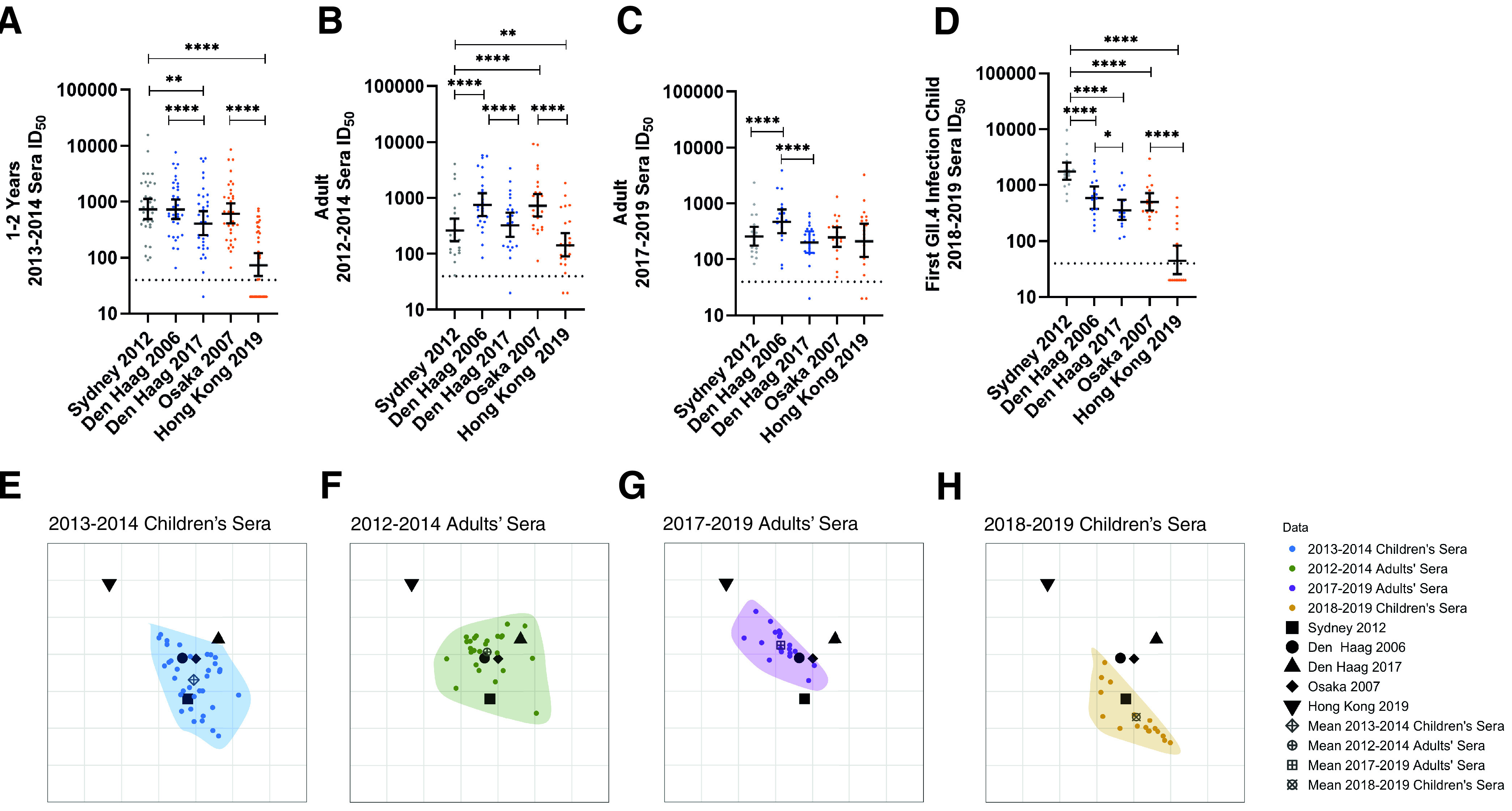
Antigenic divergence of novel strains depends on exposure history of the population. (A to D) Blockade antibody titer in sera from children aged 1 to 2 years in 2013 to 2014 (n = 34) (A), adults in 2012 to 2014 (n = 25) (B), adults in 2017 to 2019 (n = 19) (C), and children (n = 17) after their first GII.4 (Sydney 2012) infection in 2018 to 2019 (D). Marker, individual response. Line, geometric mean titer. Error bars, 95% confidence intervals. *, P ≤ 0.03; **, P ≤ 0.0021; ****, P < 0.0001, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test, compared to Sydney 2012 or between the two Den Haag VLPs or Osaka 2007 and Hong Kong 2019. (E to H) Antigenic cartography analysis across all serum sets, divided into separate panels for clarity: children in 2013 to 2014 (E), adults in 2012 to 2014 (F), adults in 2017 to 2019 (G), and children in 2018 to 2019 (H). Virus variants are represented as distinct black shapes, and each serological data set is represented by distinct colors and with data points encapsulated in a shaded polygon. The mean of the serological points for each serum set is indicated by distinct dark gray shapes. One grid box corresponds to a 2-fold change in titer. Note that the orientation of the plots does not matter.
