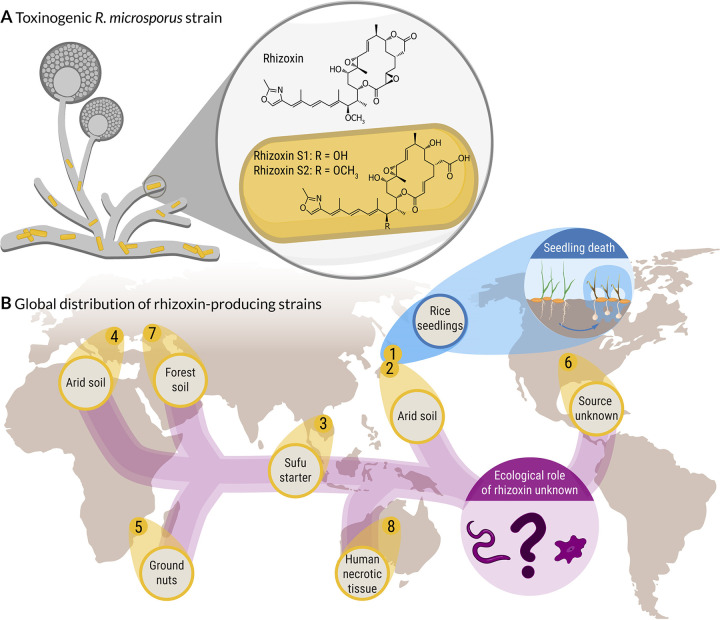
FIG 1.
Global distribution of a toxin-producing bacterial-fungal symbiosis. (A) Symbiotic bacteria (Mycetohabitans sp.) residing within the fungal hypha of R. microsporus, produce a mixture of toxic secondary metabolites (rhizoxins). (B) Rhizoxin-producing Rhizopus-Mycetohabitans strains were isolated from environmental samples from geographically distinct sites covering all five continents. In one of the eight toxinogenic strains (R. microsporus ATCC 62417, blue), rhizoxin causes blight disease in rice seedlings, while the ecological role of rhizoxin in the other, nonpathogenic Rhizopus strains is currently unknown.