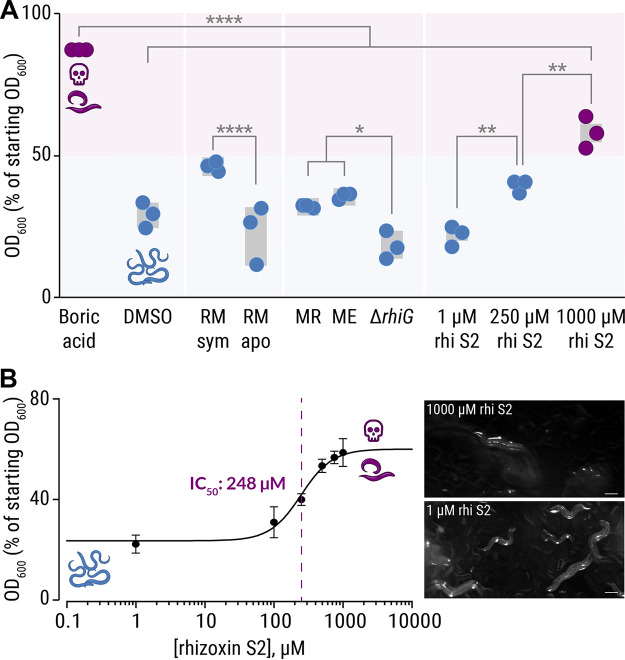
FIG 5.
Inhibitory effects of crude extracts and pure rhizoxin S2 on C. elegans. (A) C. elegans, coincubated with E. coli OP50 cells as food source, were exposed to 2% crude culture extracts from symbiotic R. microsporus (RMsym), endosymbiont-free Rhizopus microsporus (RMapo), axenically grown endosymbiotic M. rhizoxinica HKI-0454 (labeled MR), Mycetohabitans endofungorum HKI-0456 (labeled ME), and rhizoxin-deficient M. rhizoxinica (ΔrhiG), as well as pure rhizoxin S2 (rhi S2). Since the number of viable nematode worms in the suspension is directly related to the E. coli cell density, the OD600 values were plotted as a percentage of the starting OD600. Incubation with 18 mM boric acid (positive control) kills most of the nematodes (E. coli density of 80%), while exposure to crude culture extracts has a mild effect on C. elegans viability. Circles indicate independent replicated experiments (n = 3) ± 1 SEM (gray bars). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was performed (*, P < 0.03; **, P < 0.002; ****, P < 0.0001; see Table S4). (B) Liquid feeding inhibition assay of C. elegans supplemented with the bacterial rhizoxin S2. Data points represent three independent replicated experiments (n = 3) ± 1 SEM. Microscopic images of nematodes exposed to pure rhizoxin S2 are shown. Scale bars, 200 μm.