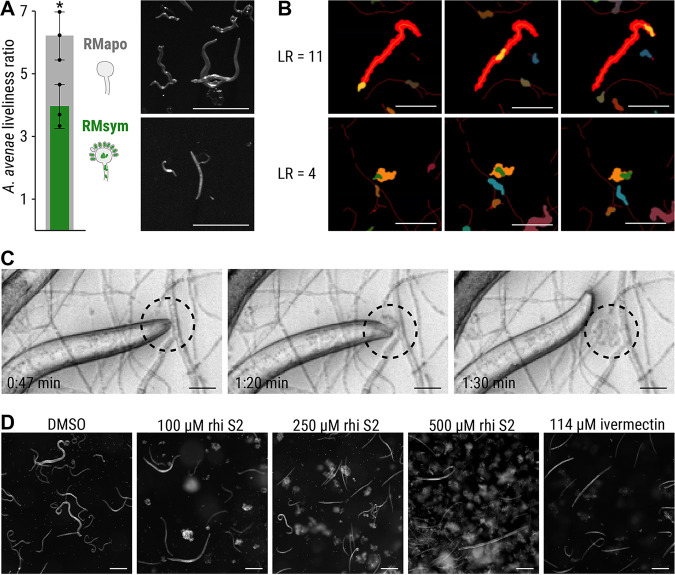
FIG 6.
Feeding inhibition of A. avenae on R. microsporus. (A) A. avenae was coincubated with symbiotic R. microsporus (RMsym) or endosymbiont-free R. microsporus (RMapo) for 2 to 3 weeks. Nematode movement was recorded using a stereomicroscope with a frame rate of 1 fps. The liveliness of the worms was calculated from the ratio of the area covered by a worm, divided by the area of the worm itself, and scaled to the full length of the movie. The minimum scaled liveliness ratio (LR) for a live worm was set to 1.5, below this value the worm was declared inactive/dead. n = 3 independent replicated experiments ± 1 SEM. An unpaired t test with Welch’s correction was performed (*, P < 0.05; see Table S5). Microscope images of A. avenae used for analysis. Scale bars, 500 μm. (B) Illustrations of the LR at high (top) and medium (bottom) values. (Top) The worm shown in orange covers the red footprint area during the time course of the experiment. These images show the first (left column), middle (middle column), and final (right column) time points of the movie. The activity of a worm was characterized by dividing the endpoint footprint by the area of the worm at each time point. The resulting LR was 11.5 for the worm in the top row, thus indicating a very active nematode. (Bottom) A less active worm (green area) covered a smaller footprint (orange area), as shown by the LR value of 4.0. Scale bars, 300 μm. See the live videos of the segmented worms and their footprints in Videos S11 and S12 (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6827988) for the worms with LR = 11.5 and LR = 4.0, respectively. (C) Time-lapse images of A. avenae feeding on endosymbiont-free R. microsporus (black circle). Endosymbiont-free R. microsporus ATCC 62417/S was coincubated with A. avenae for 24 h in a microchannel slide (Ibidi), and feeding was recorded on a spinning disc microscope (see Movie S1). Scale bars, 20 μm. No feeding was observed in worms that were coincubated with symbiotic R. microsporus (see Fig. S1D; see also Video S2 [https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6827988]). (D) Microscopic images of A. avenae after exposure to different concentrations of pure rhizoxin S2 (rhi S2). Worms were healthy and alive when exposed to the solvent control (DMSO). Exposure to 114 μM ivermectin killed all worms. See the live videos of nematode movement in Videos S3 to S7 (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6827988). Scale bars, 200 μm.