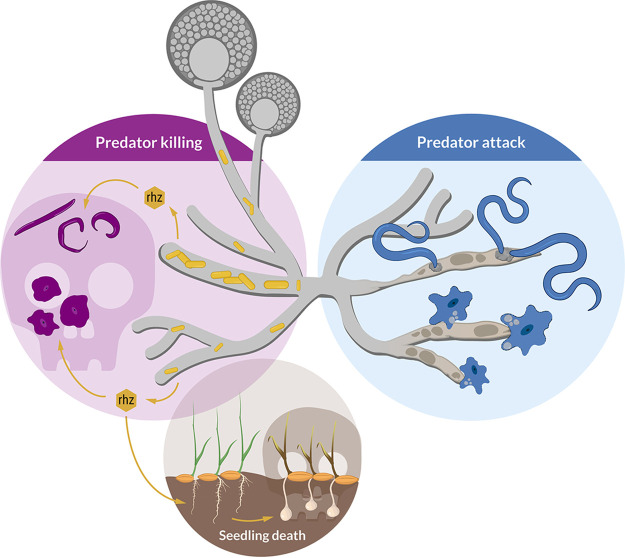
FIG 7.
Schematic model of the ecological role of rhizoxin-producing endofungal bacteria (M. rhizoxinica). The fungal host (Rhizopus microsporus) utilizes the bacterial secondary metabolite rhizoxin to fend off fungivorous micropredators such as amoeba and nematodes. The absence of endofungal bacteria leads to R. microsporus being attacked and subsequently killed by protozoan and metazoan predators. The establishment of the Rhizopus-Mycetohabitans symbiosis may have first developed to provide protection against fungal predators, with the emergence of plant pathogenicity developing later.