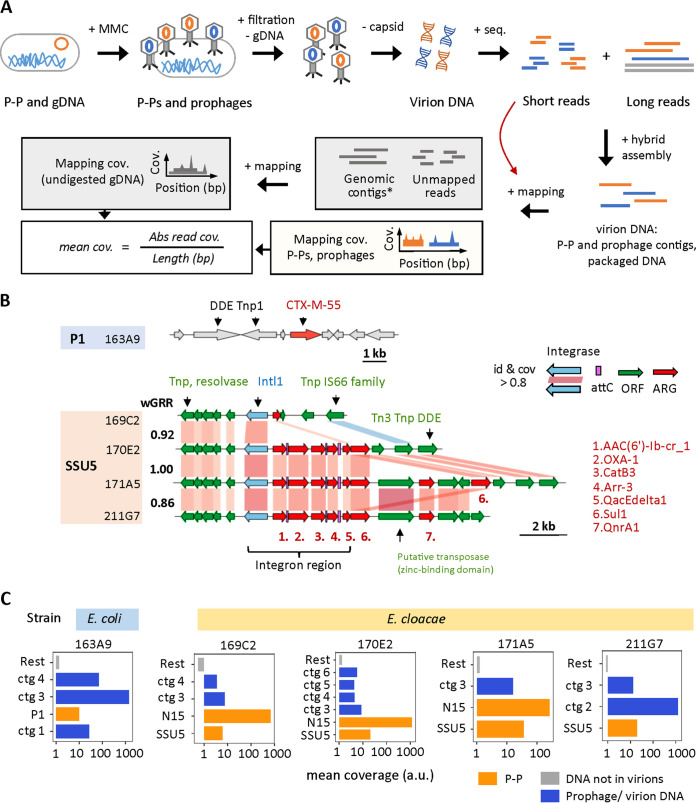
FIG 4.
Induction of P-Ps and prophages in CRE strains. (A) CRE strains with ARG-encoding P-Ps were induced by 5 μg/mL MMC. 4 h after induction, phage particles were purified, and chromosomal DNA (gDNA) was removed by DNase I digestion. The phage capsid was degraded by proteinase K, and the virion DNA was purified and sequenced. The obtained short reads were coassembled with long reads from the genomic sequencing experiment (see Materials and Methods). The assemblies were compared to P-P and phage genomes and subsequently assigned. The read mapping coverage was computed (by mapping the short reads from the MMC experiment on them). The reads that did not map to the assemblies were used to compute the background coverage caused by the undigested gDNA (by mapping to genomic contigs obtained via the long read assembly). (B) In the genome of the P1-like P-P of the E. coli 163A9, the CTX-M-55 gene is found next to two DDE transposases. The ARGs encoded in the SSU5-like P-Ps from the E. cloacae strains 169C2, 170E2, 171A5, and 211G7 are in a complex region containing transposases and integrons. Homology assignments between P-Ps were done when the sequence similarity was at least 80% identity and covered 80% of the sequence of the gene (retrieved from an all-versus-all BLASTP comparison). The similarity between P-Ps is indicated by the weighted gene repertoire relatedness (wGRR). (C) The average read coverage was obtained and calculated as described in panel A. All contigs (= ctg) larger than 10 kb are shown. The coverage (a.u.: arbitrary unit) is plotted on a logarithmic x axis for the P-P contigs (P1 = P1-like, SSU5 = SSU5-like, N15 = N15-like) (orange), the contigs assigned to prophages or virion loaded DNA (blue), and the average background coverage (the rest of the coverage) obtained after mapping the remaining reads to genomic contigs (gray) for each tested CRE strain.