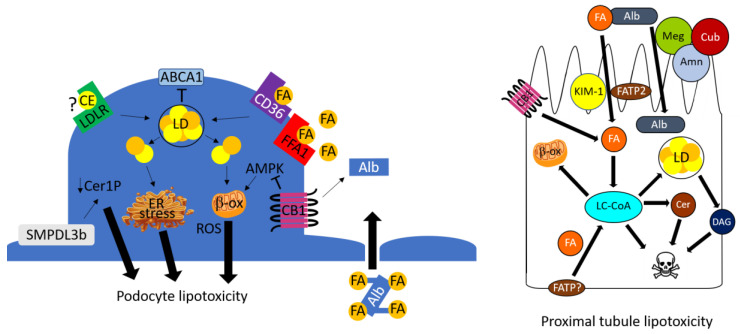
Figure 1.
Lipotoxicity in the podocyte. Under pathologic (albuminuric) circumstances, fatty acids and cholesterol esters are taken up by separate mechanisms. If the accumulated lipids exceed storage capacity within lipid droplets, toxic metabolites accumulate and lead to reactive oxygen species generation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately podocyte cell death. Abbreviations: albumin (Alb), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), ATP-binding cassette A1 (ABCA1), cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), ceramide-1-phosphate (Cer1P), cholesterol ester (CE), endoplasmic reticulum (ER), fatty acid (FA), free fatty acid receptor-1 (FFA1), lipid droplet (LD), low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), reactive oxygen species (ROS), acid sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b (SMPDL3b).