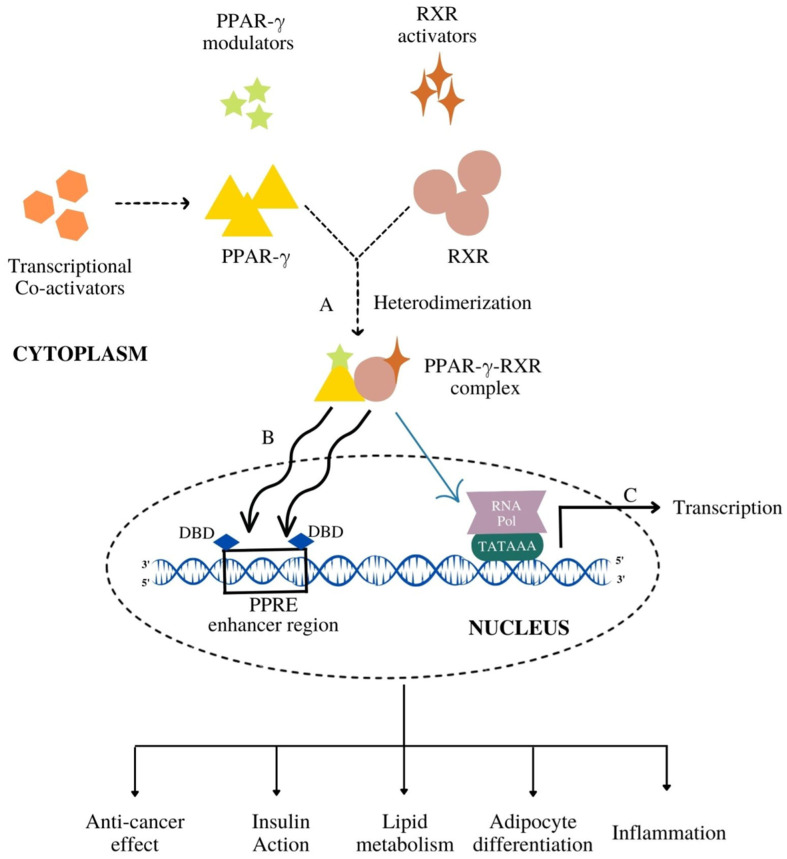
Figure 3.
The mechanism of PPAR-γ activation followed by the gene transcription. (A) PPAR-γ upon binding with its modulators (endogenous, natural, synthetic) heterodimerize with RXR to form PPAR-γ-RXR heterodimerized complex. (B) This complex gets translocated inside the nucleus and binds to the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of PPAR response elements (PPRE) enhancer region. (C) Such a binding leads to the transcriptional activation of target genes resulting in various metabolic cascades such as insulin action, lipid metabolism and anti-cancer effects.