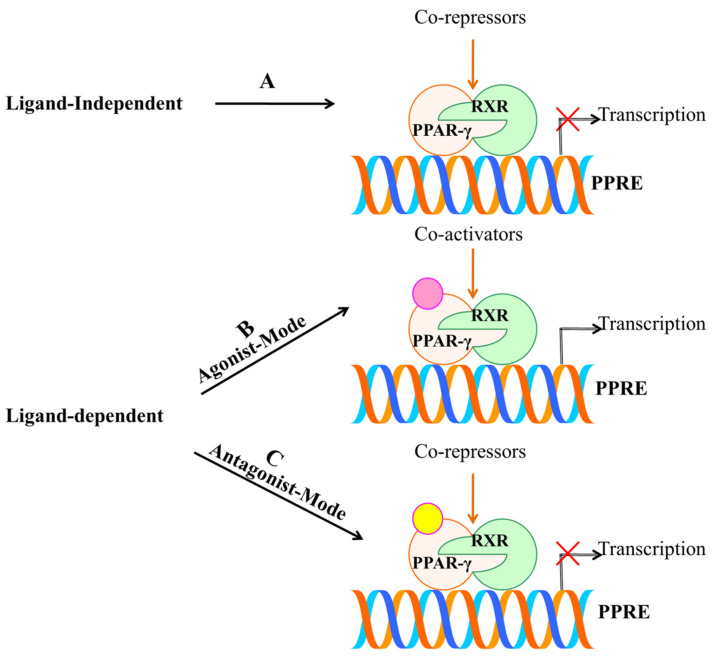
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of activation of PPAR-γ receptor through ligand-dependent or -independent mechanisms. (A) Ligand-independent mechanism does not involve the active participation of ligand, and co-repressors bind to unliganded PPAR-γ, which repress the gene expression by chromatin remodeling. (B) Agonist mode of action involves the binding of ligand to LBD of PPAR-γ with the help of co-activators, which further leads to transcription of targeted genes. (C) Antagonist mode of action also involves the binding of ligand without leading to transactivation activity, due to the presence of co-repressors.