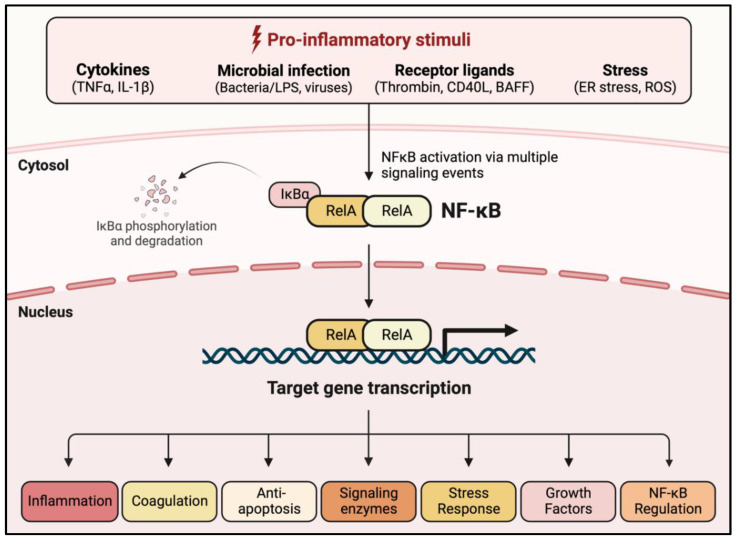
Figure 3.
NF-κB activators and cell responses. Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is activated by proinflammatory stimuli including cytokines (tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β)), microbial infection (bacteria/lipopolysaccharide (LPS), viruses), receptor ligands (thrombin, CD40 ligand (CD40L), B-cell-activating factor (BAFF)), and stress (endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, reactive oxygen species (ROS)). Stimulation liberates the NF-κB dimer secondary to degradation of IκBα (inhibitor of κB) in the cytosol and promotes its nuclear translocation and DNA binding to activate transcription of genes involved in numerous cell responses.