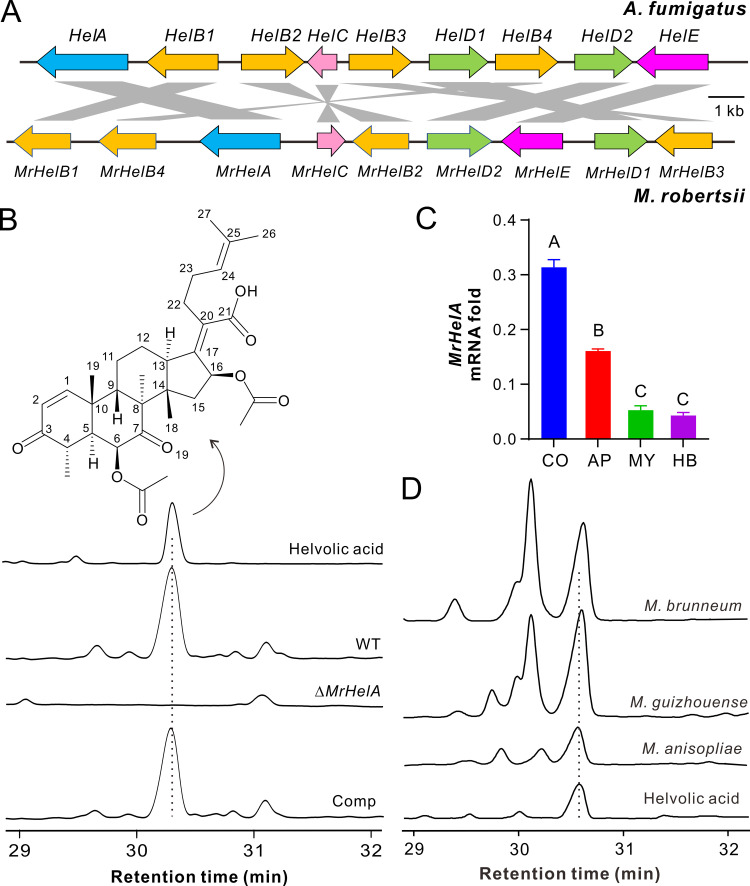
FIG 1.
Conservative production of helvolic acid (HA) by different Metarhizium species. (A) Mesosyntenic relationship between the HA BGCs in A. fumigatus and M. robertsii. Gene models in the same color represent coding of proteins in a family. The putative function of each gene is listed in Table S1. (B) Verification of HA production by M. robertsii. Comp, complemented strain of the ΔMrHelA mutant. The WT and mutant strains were used to infect last-instar larvae of the wax moth, and the mycosed insect cadavers were extracted with ethyl acetate for HPLC analysis. (C) Differential expression of MrHelA by M. robertsii. CO, conidia harvested from the 2-week-old PDA plates; MY, mycelia harvested from the 3-day-old SDB culture; AP, appressorium cells induced on soldier fly wings for 18 h; HB, hyphal body cells harvested from the hemolymph of Galleria larvae after injection for 3 days. Values are means and standard deviations (SD). The difference between samples was determined by one-way ANOVA. Different letters above columns indicate differences with a P value of <0.01. (D) Verification of HA production by different Metarhizium species. The fungi were inoculated on rice medium for 2 weeks for metabolite extractions.