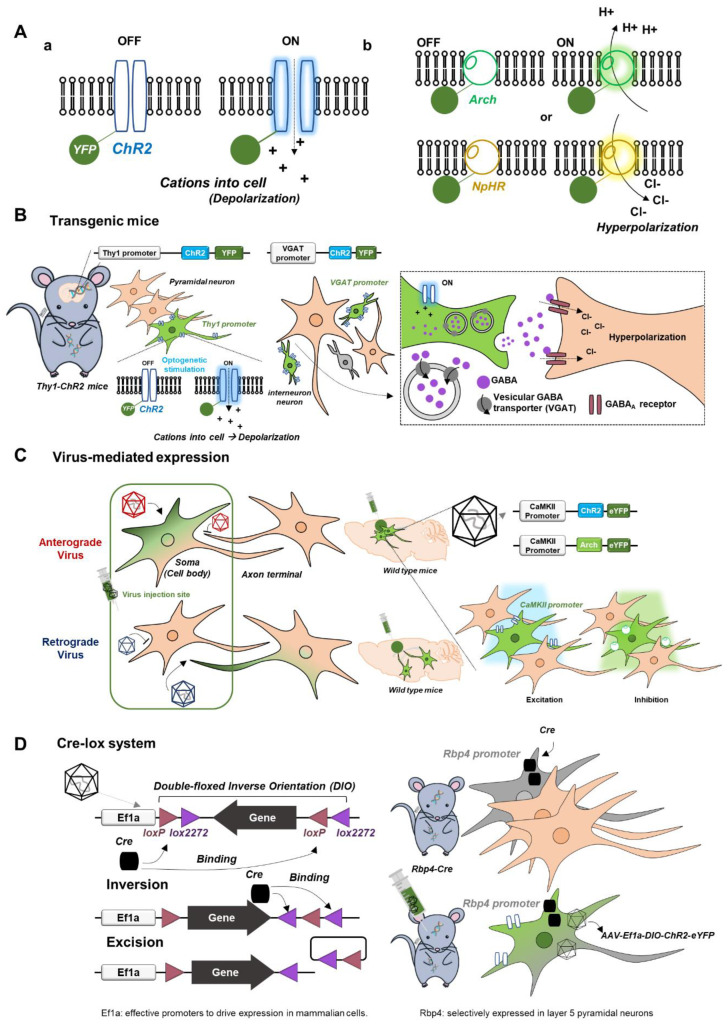
Figure 1.
Basics of optogenetics relevant to fMRI. (A) Light-sensitive opsins. Channelrhodopsin2 (ChR2; nonspecific cation channel), a representative excitatory opsin, which causes membrane depolarization (a). Inhibitory opsins such as halorhodopsin (NpHR; inward chloride pump) and archaerhodopsin (Arch; outward proton pump), which cause membrane hyperpolarization (b). (B–D) Three different approaches for the expression of light-sensitive opsins. (B) Transgenic mice with opsins in cell-type specific neurons. Transgenic Thy1-ChR2 mice for optogenetic excitation of pyramidal neurons. Transgenic VGAT-ChR2 mice for optogenetic inhibition of pyramidal neurons. (C) Virus-mediated expression of opsins for promotor-based gene delivery into neurons. Anterograde infection from cell bodies to axon terminals. Retrograde infection from axon terminals to cell bodies. (D) Cre-lox system for site- and cell-specific optogenetics. Diagram of the double-floxed inverse orientation (DIO) transgenic system.