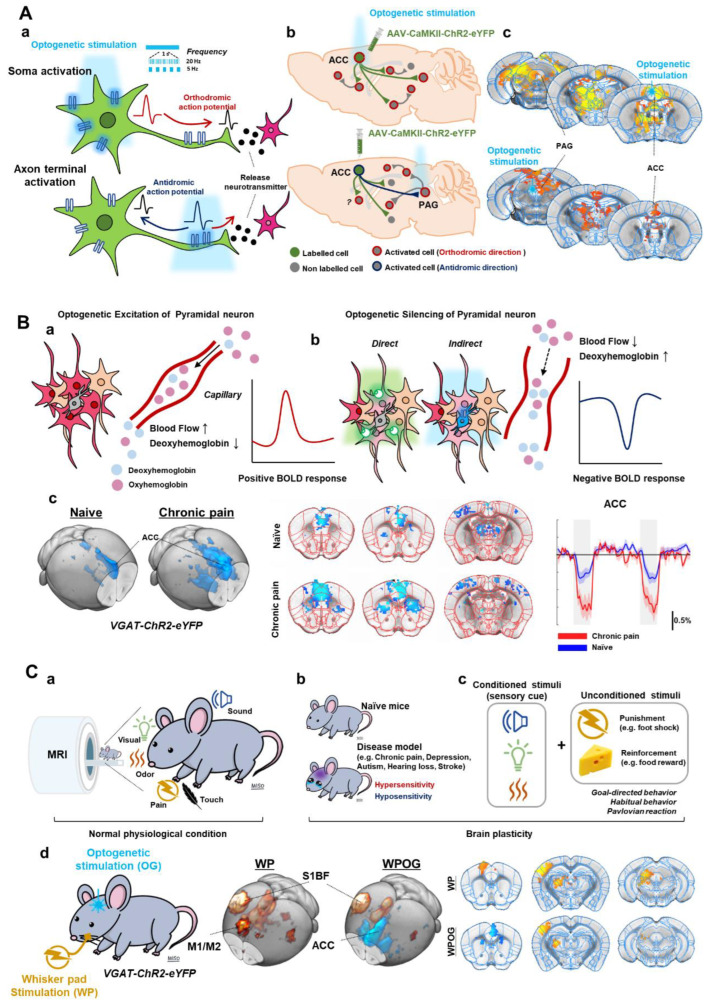
Figure 2.
Optogenetic strategies for fMRI. (A). Optogenetic stimulation of excitatory cell bodies (soma) or axon terminals. Orthodromic and antidromic propagation responding to the stimulating site (a). Postsynaptic activities by optogenetic stimulation (b). ofMRI response maps induced by optogenetic stimulation; fMRI response map by cell body stimulation of ACC and by axon terminal stimulation of ACC-PAG projection (c). (B). Optogenetic silencing by inhibitory opsins in excitatory pyramidal neurons (a) or excitatory opsins in inhibitory interneurons (b). ofMRI response of naïve and CFA-induced chronic pain model mice during ACC inhibition (c). (C). Combining optogenetics with sensory-evoked fMRI. fMRI with sensory stimuli (sensory-evoked fMRI) (a). Applying sensory-evoked fMRI to animal disease models (b) or conditioning behaviors (c). Silencing ofMRI combined with electrical stimulation (d). Adapted with permission from Lee et al. (2022) [20]. ACC; anterior cingulate cortex, PAG; periaqueductal gray.