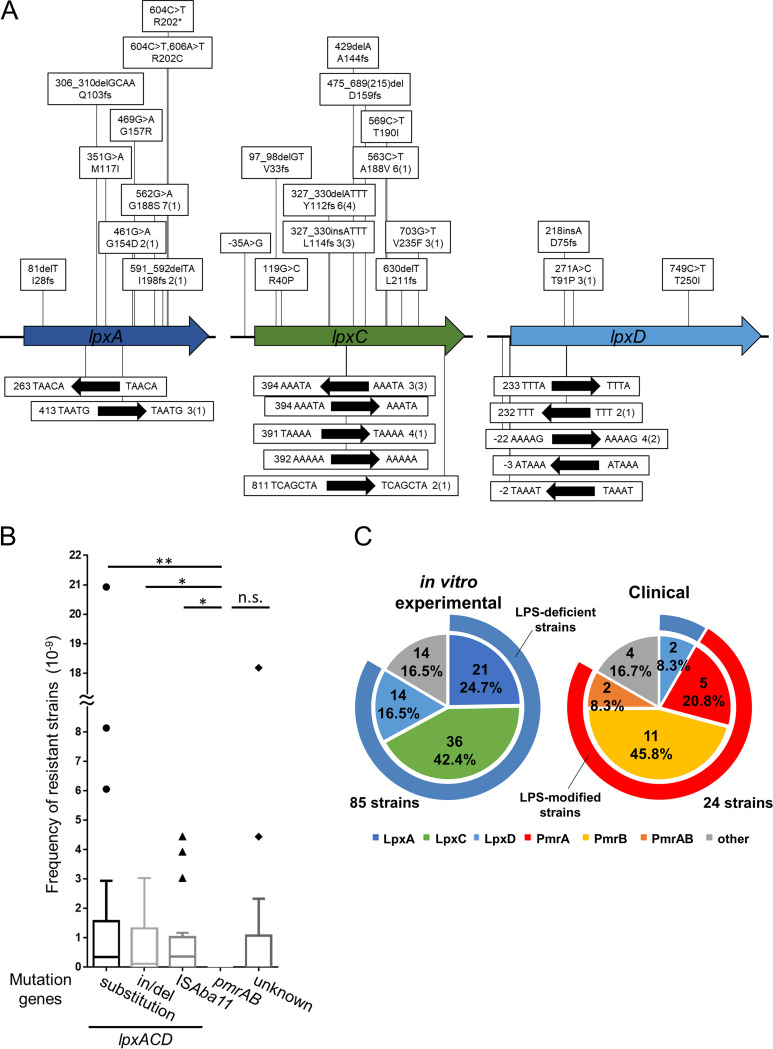
FIG 1.
Mutation sites of colistin-resistant A. baumannii strains in laboratory and clinical settings. (A) Mutation site analysis of in vitro experimental laboratory-isolated strains. A. baumannii ATCC 19606 strains were isolated by direct plating on LB agar plates containing 5× MIC of colistin (10 μg/mL) to select resistant strains. Sanger sequencing was performed on the genomic regions containing the lpxACD genes. In the boxes above the genes, base changes are shown on top, while amino acid changes are shown below. The numerical values are the numbers of isolated strains, and numbers in parentheses are the numbers of independent events. The black arrows indicate ISAba11, and repetitive sequences are shown. (B) Frequency analysis of occurrence for each mutation. Data are shown in a box plot; 18 independent assays were compared by one-way ANOVA. n.s., not significant; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. Of the 110 colistin-resistant strains, 28 could not be sequenced because of overlapping colonies. (C) Pie chart showing mutation rates. Data for isolated in vitro experimental strains are on the left, and the results of NCBI BioSample analysis are on the right.