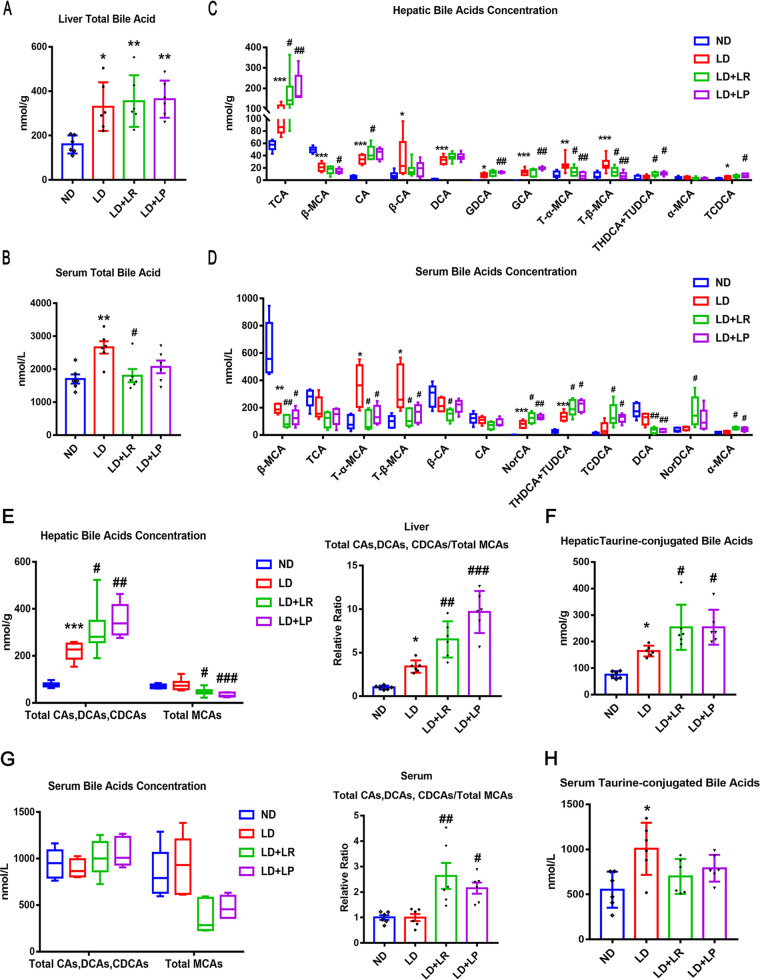
FIG 2.
L. reuteri (LR) and L. plantarum (LP) treatments changed the bile acid species in the liver and serum. The mice in each group were sacrificed at the end of the 8th week, and serum and liver were collected. (A) Total bile acids (TBA) in the livers of mice. (B) TBA in the serum of mice. (C) The top 12 most abundant hepatic BA species were analyzed. (D) The top 12 most abundant serum BA species are shown. NorCA, norcholic acid; NorDCA, 23-nordeoxycholic acid. (E) Total CAs, DCAs, and CDCAs, total MCAs, and ratios of total CAs, DCAs, and CDCAs to total MCAs in the livers. (F) Total taurine-conjugated BAs in the livers. (G) Total CAs, DCAs, and CDCAs, total MCAs, and ratios of total CAs, DCAs, and CDCAs to total MCAs in the serum. (H) Total taurine-conjugated BAs in the serum. Data were analyzed by ANOVA along with the post hoc Tukey test and are presented as the mean values ± SEM (n = 6). *, 0.01 < P ≤ 0.05; **, 0.001 < P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001 versus normal diet (ND) group; #, 0.01 < P ≤ 0.05; ##, 0.001 < P ≤ 0.01; ###, P ≤ 0.001 versus lithogenic diet (LD) group.