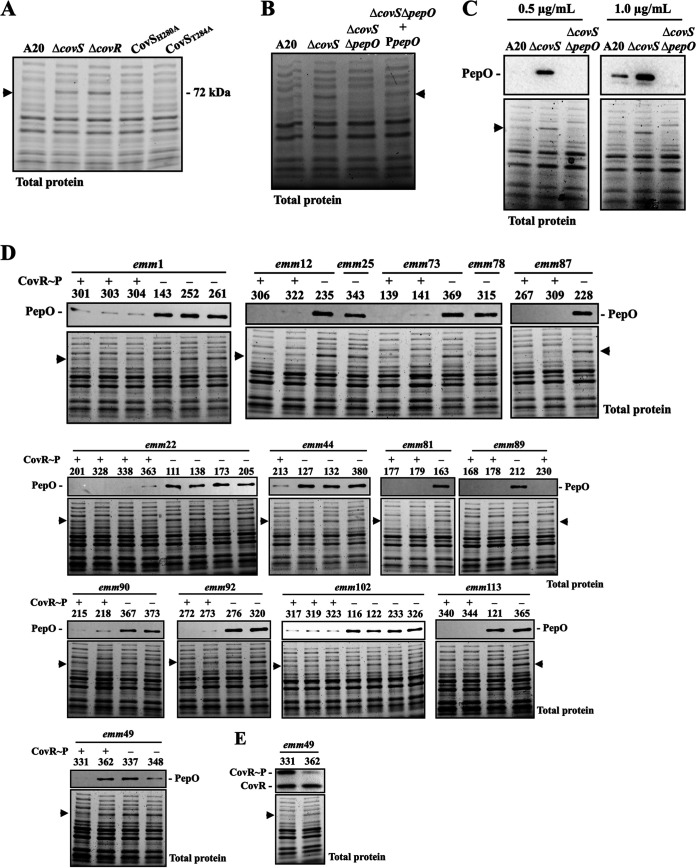
FIG 3.
Identification and verification of the 70- to 72-kDa protein marker in the covR/covS mutants and the CovR/CovS-activated and -inactivated isolates. (A) Total protein profiles of the wild-type A20 strain, covS mutant (ΔcovS), covR mutant (ΔcovR), CovS kinase-inactivated mutant (CovSH280A), and CovS phosphatase-inactivated mutant (CovST284A). (B) Total protein profiles of A20, covS mutant (ΔcovS), covR mutant (ΔcovR), covS/pepO double mutant (ΔcovS/ΔpepO), and pepO trans-complementary strain (ΔcovS/ΔpepO+PpepO). (C) Western blot of PepO expression in A20, covS mutant (ΔcovS), and covS/pepO double mutant (ΔcovS/ΔpepO) detected by the anti-PDTTYYEEGNEKAEELR antibody. (D) Comparison of PepO expression in CovR/CovS-activated and CovS-inactivated clinical isolates. The PepO protein was detected by the anti-PDTTYYEEGNEKAEELR antibody in a total protein extract. (E) Phosphorylation levels of CovR in the emm49 SPY331 and SPY362 isolates. CovR~P denotes phosphorylated CovR; CovR denotes non-phosphorylated CovR. Arrows indicate when a signal from only the CovR/CovS-inactivated mutants was identified. The lower sections of the image in panels C, D, and E show total protein as the loading control.