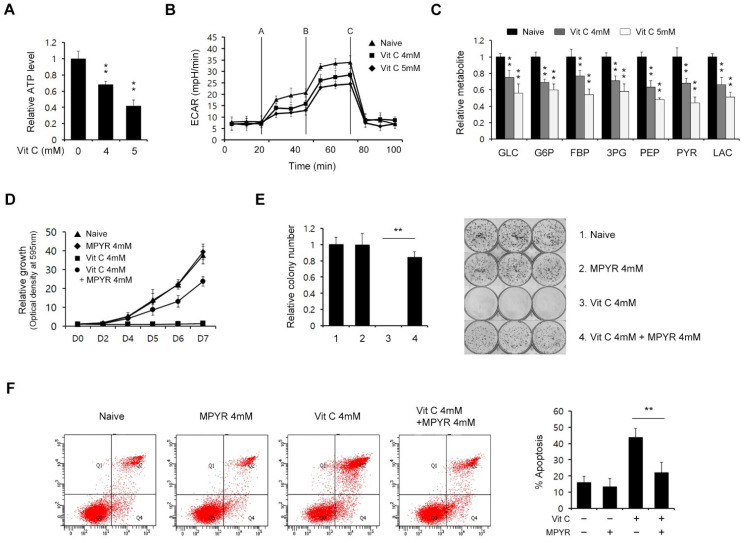
Figure 3.
High-dose vitamin C suppresses the glycolytic flux in PDAC cells. (A) 8988T cells were treated with vitamin C (4 or 5 mM) for 24 h and assayed for intracellular ATP. (B) 8988T cells were treated with vitamin C (4 or 5 mM) for 24 h, and the extracellular acidification rate was measured. (C) 8988T cells were treated with vitamin C (4 or 5 mM) for 24 h and analyzed for glycolysis metabolite pools via LC/MS-MS. (D) Cell growth assay for 8988T cells treated with vitamin C (4 mM) for 8 days with or without methyl-pyruvate (4 mM). (E) Clonogenic assay for 8988T cells treated with vitamin C (4 mM) for 8 days with or without methyl-pyruvate (4 mM). Error bars represent the s.d. of triplicate wells from a representative experiment. (F) 8988T cells were treated with vitamin C (4 mM) for 8 days with or without methyl-pyruvate (4 mM) and assayed for apoptotic cell death by annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry. Error bars represent the s.d. of triplicate wells from representative experiments; ** p < 0.01.