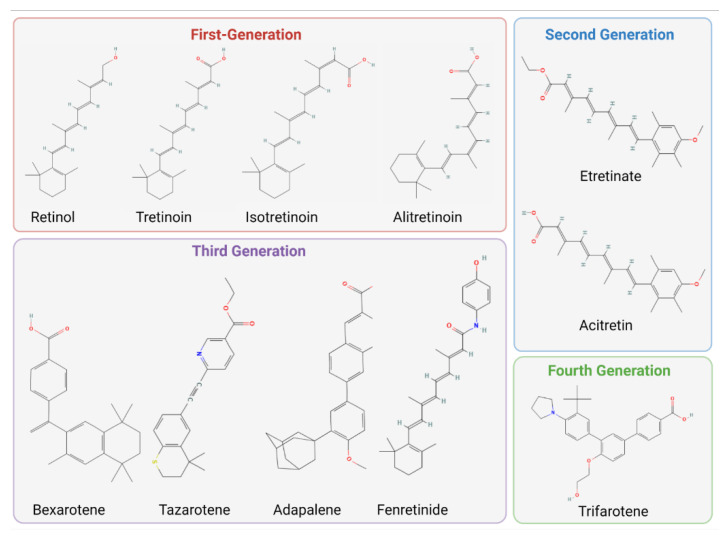
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of clinically used retinoids from each generation. 2D-Structures taken from Pubchem.com. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Retinol#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tretinoin#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Alitretinoin (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Isotretinoin#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Etretinate (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Acitretin#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Bexarotene#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tazarotene#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Adapalene#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Fenretinide#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022); https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Trifarotene#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 19 September 2022). Figure generated with Biorender.com.