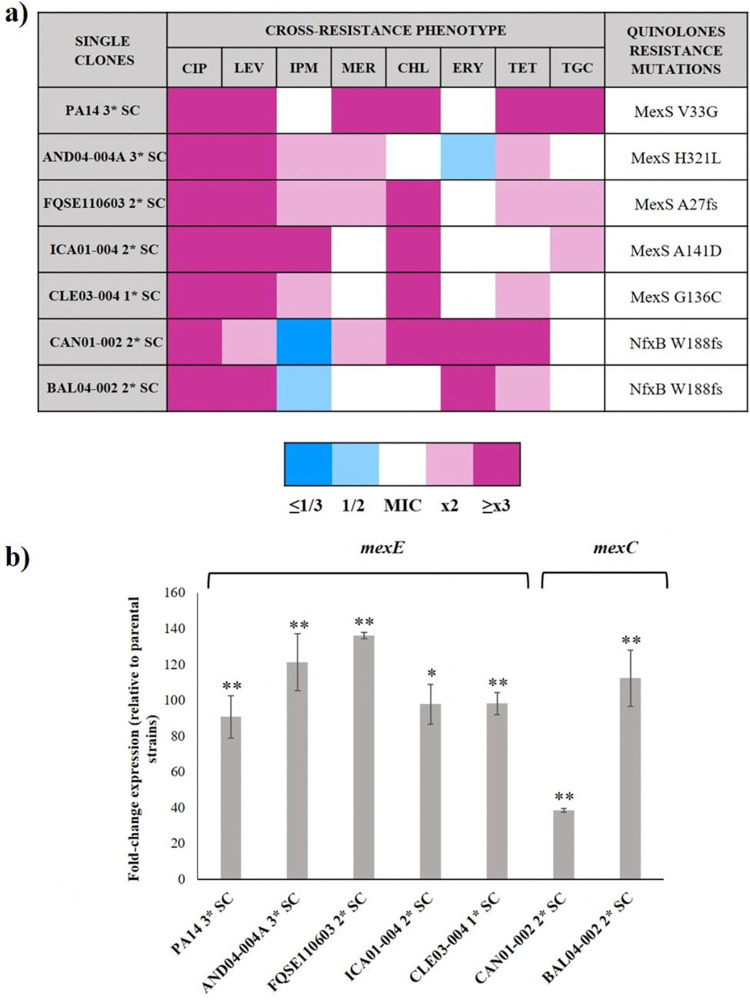
FIG 3.
Cross-resistance phenotype and efflux pumps’ implication in P. aeruginosa clones evolved under ciprofloxacin risk concentration. Representative multidrug-resistant clones derived from populations of P. aeruginosa PA14 and 6 clinical isolates evolved under 0.04 μg/mL of ciprofloxacin for 3 days (1*–3* single clone [SC]) were chosen for sequencing genes likely involved in quinolones resistance and measuring their expression level. (a) Cross-resistance phenotype and detected quinolones resistance mutations in the representative clones. MIC values and specific nucleotide changes are enclosed in Table S4. (b) mexE and mexC expression of the analyzed clones. Fold changes were estimated with respect to the value of each parental strain. As shown, the analyzed clones overexpress either mexE or mexC. Error bars indicate standard deviations of the results from three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences in the expression level between the analyzed clones and their parental strains were assessed using the Student’s t test and are shown (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005). CIP, ciprofloxacin; LEV, levofloxacin; IPM, imipenem; MER, meropenem; CHL, chloramphenicol; ERY, erythromycin; TET, tetracycline; TGC, tigecycline.