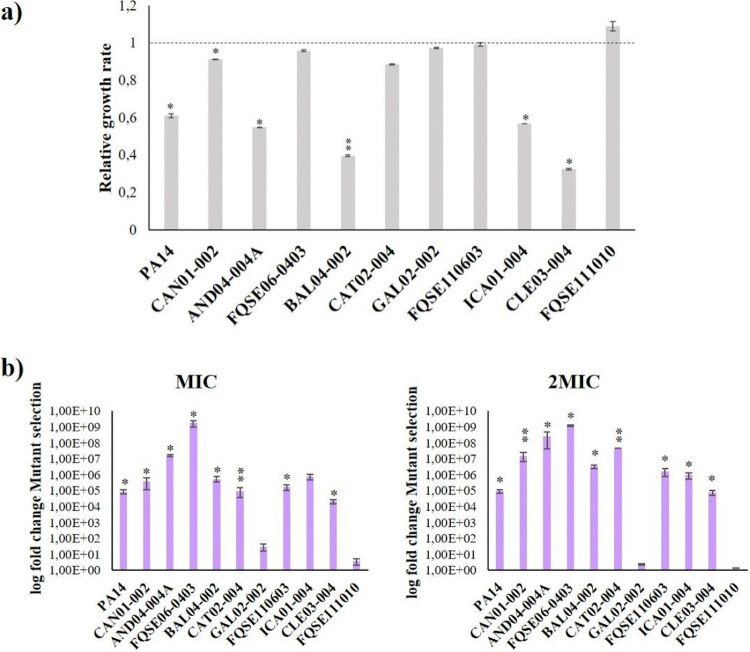
FIG 4.
Fitness and mutant selection of P. aeruginosa clinical isolates in the presence of ciprofloxacin risk concentration. (a) Relative fitness of P. aeruginosa PA14 and 10 clinical isolates grown for 30 h in the presence of 0.04 μg/mL of ciprofloxacin, with respect to the ones grown in LBB for the same interval (dotted line). (b) Relative mutant selection of P. aeruginosa PA14 and 10 clinical isolate populations evolved under 0.04 μg/mL of ciprofloxacin for 3 days, with respect to the ones evolved in LBB for the same interval. Mutant selection was uncovered in the presence of MIC and twice the MIC of ciprofloxacin for each strain. In order to calculate fold changes, mutant selection <10−10 was considered as 10−10. In both assays (a and b), error bars indicate standard deviations from three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences were assessed using the Student’s Student’s t test and are shown (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005).