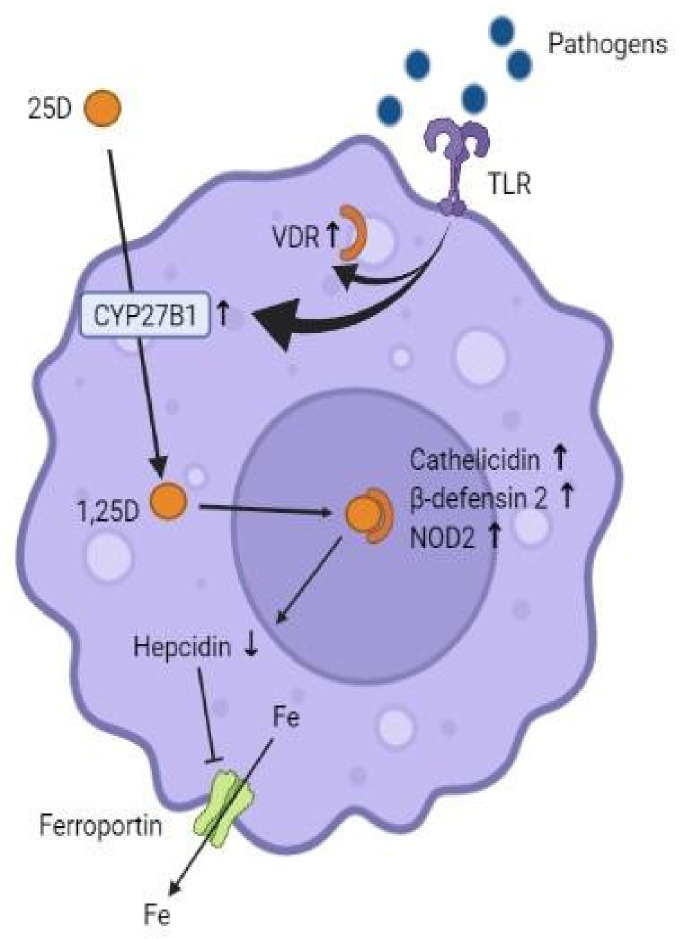
Figure 1.
Effects of vitamin D on immune cells. Activation of toll-like receptors (TLRs) by pathogens increases the expression of VDR and CYP27B1. 1,25(OH)2D3 binds to VDR, which induces the formation of cathelicidin, β-defensin 2 and NOD2. Vitamin D suppresses hepcidin, which facilitates the outflow of intracellular iron (Fe).