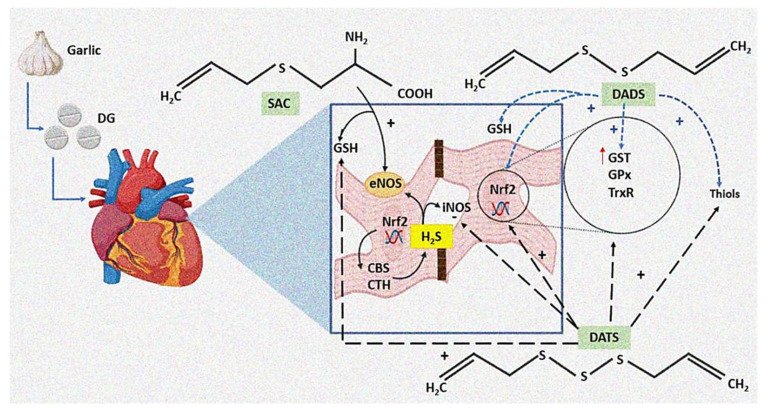
Figure 6.
Mechanisms by which DG treatment may down-regulate the negative inotropic and chronotropic effects in the heart in sepsis. A possible mechanistic explanation for the beneficial effect of the DG treatment on the heart is through the H2S production. The active organic polysulfides, such as SAC, DADS, and DATS, which are provided by DG, act as H2S donors in the presence of thiols and GSH through an increase in the CBS and CTH activity. These polysulfides could also increase the expression of Nrf2 that modulates the overexpression of the antioxidant enzymes, such as eNOS, GST, GPx, and TrxR. Abbreviations: SAC = S-allyl-cysteine, DAS = diallyl sulfide, DATS = diallyl trisulfide, Nrf2 = nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, CBS = cystathionine β-synthetase, CTH = cystathionine γ-lyase, GSH = glutathione, iNOS = inducible nitric oxide synthase, H2S = hydrogen sulfide synthesis, eNOS = endothelial nitric oxide synthase, DG = deodorized garlic, TrxR = thioredoxin reductase, GPx = glutathione reductase, GST = glutathione-S-transferase.