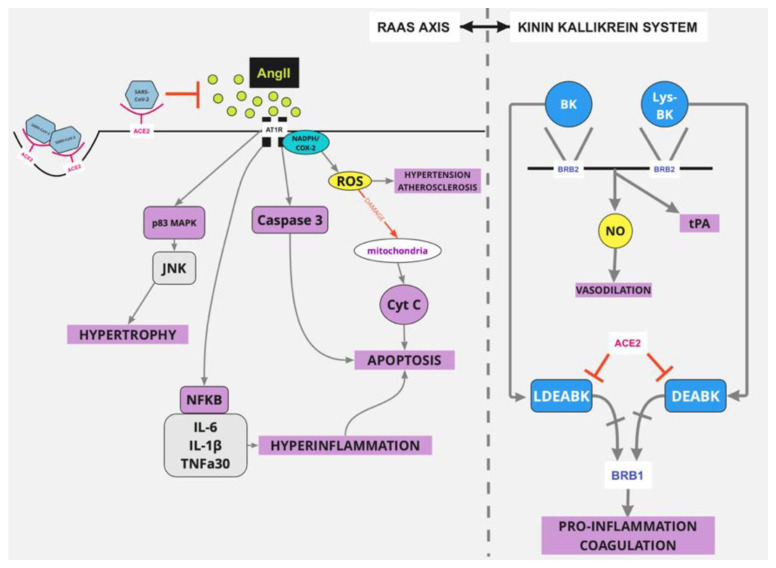
Figure 3.
SARS-CoV-2 infection and alterations in the RAAS and KKS axis. SARS-CoV-2 binds to the ACE2 receptor causing its internalization. ACE2 no longer converts AngII to Ang1-7 and AngII binds to the AT1 receptor and subsequently triggers the production of p83 MAPK, caspase 3, ROS and Cyt C, which promotes apoptosis, hyperinflammation and hypertrophy. ACE2 also affects the KKS axis by affecting DEABK’s and LDEABK’s attachment to BRB1, thus leading to inflammation and coagulation. Abbreviations used: RAAS: Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System; AT1R: Angiotensin type 1 receptor; p83 MAPK: p83 mitogen activated protein kinase; Cyt C: Cytochrome C; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; KKS: Kinin-Kallikrein system; DEABK: [des-Arg9]-BK; LDEABK: Lys-[des-Arg9]-BK; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; COX2: cyclooxygenase 2; IL-6, IL-1β, TNFa30: proinflammatory cytokines; BRB1/2: bradykinin receptor B1/B2; BK: bradykinin; Lys-BK: Lys- bradykinin.