Figure 3:
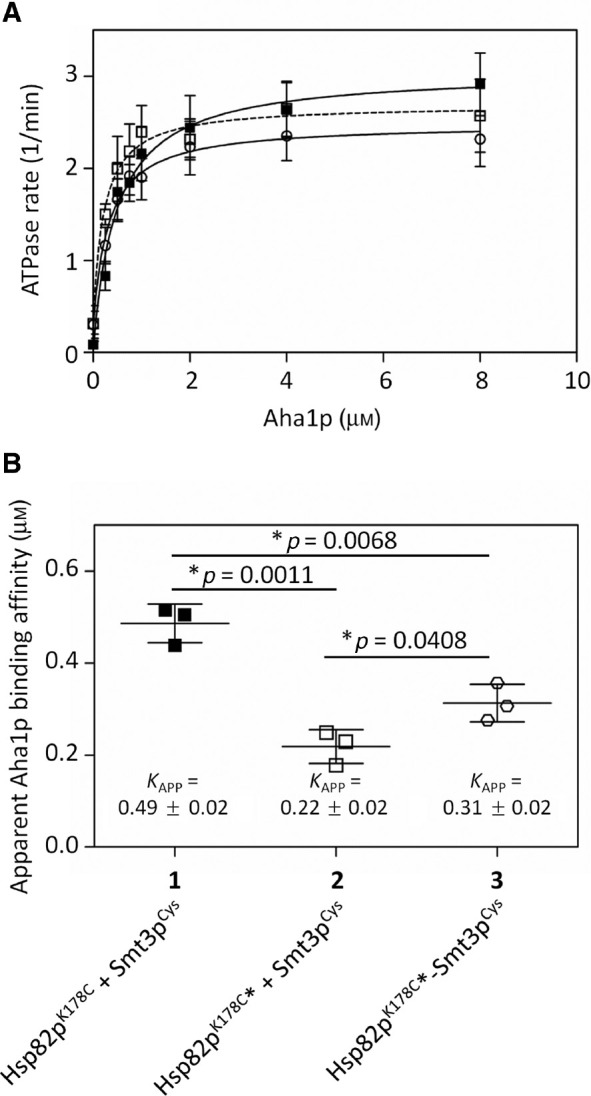
Aha1p-mediated stimulation of SUMOylated Hsp82p.
(A) Aha1p titration into non-SUMOylated Hsp82p, derivatized but non-SUMOylated Hsp82p, and SUMOylated Hsp82p. All reactions contained 1 μm non-SUMOylated Hsp82pK178C, either treated with DMSO [Hsp82pK178C + Smt3pCys (1; black squares)] or derivatized with BMOE and quenched with DTT prior to Smt3pCys addition [Hsp82pK178C*+Smt3pCys (2; white squares)], or SUMOylated [Hsp82pK178C*-Smt3pCys (3; white circles)] and the indicated concentration of Aha1p. This experiment was carried out three times (n=3) in triplicate. (B) The apparent binding affinity (K app) of Aha1p for non-SUMOylated (1), derivatized but not SUMOylated (2), and SUMOylated Hsp82p (3) was calculated to be 0.49±0.02 μm, 0.22±0.02 μm, and 0.31±0.02 μm, respectively. Statistical significance was determined with an unpaired t-test between columns. The apparent affinity for Aha1p was calculated from the individual ATPase assays in (A) using Michaelis-Menton kinetic analysis on Prism GraphPad. Each scatter plot shows the average and standard deviation from three experiments (n=3).
