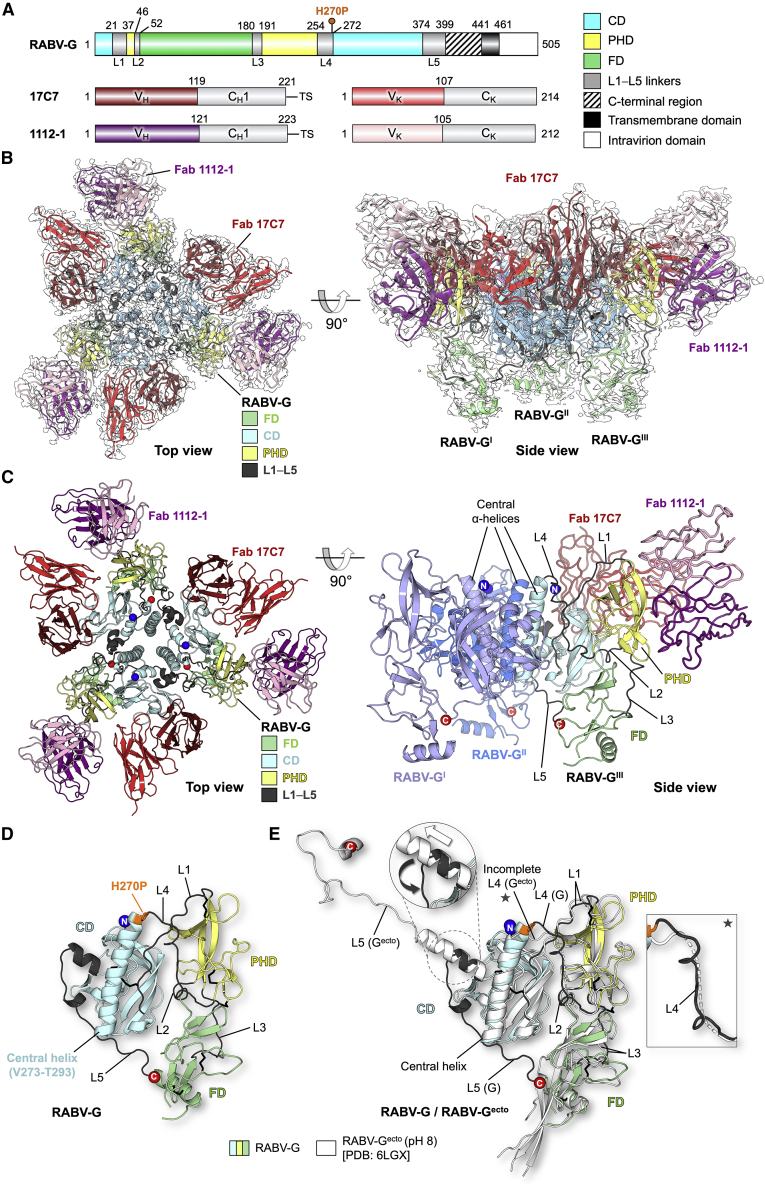
Figure 1.
Structure of pre-fusion RABV-G trimer in complex with Fabs 17C7 and 1112-1
(A) Schematic of RABV-G domain boundaries. Linear map of RABV-G protein sequence is drawn to scale using DOG software (Ren et al., 2009), with domains colored as indicated in the legend, showing “palindromic” architecture typical of class III fusion proteins (CD, central domain; PHD, pleckstrin homology domain; FD, fusion domain). The H270P point mutation in our protein construct is indicated with a pin above the map. C-terminal region (shaded) is unresolved in our structure. (Bottom) Linear maps of Fabs 17C7 and 1112-1 heavy and kappa light chains, colored and labeled accordingly. VH, VK, CH1, and CK denote the antibody variable heavy, variable kappa light, constant 1 heavy, and constant kappa light-chain domains, respectively. TS, TwinStrep tag.
(B) 2.8-Å cryo-EM map with the resulting structure of trimeric RABV-G shown in top and side view orientations. Single copies of 17C7 and 1112-1 were observed to bind to each protomer of RABV-G. The atomic model is fitted into the corresponding cryo-EM map (white) and colored according to domain with the variable regions of Fab 17C7 and Fab 1112-1 colored red and purple (darker shade for heavy chain, lighter shade for light chain), respectively. The constant regions of the Fabs were disordered in the reconstruction and therefore were not built.
(C) Atomic model of the RABV-G-Fab 17C7-Fab 1112-1 complex. (Top view) The protein molecules are displayed in cartoon representation and colored accordingly as labeled. N- and C-termini are shown as blue and red spheres, respectively. (Side view) Only one copy of each Fab is shown in ribbon representation. Two RABV-G protomers are colored blue and light purple for visual clarity. The remaining copy is colored as shown in top view.
(D) Conformational features revealed by atomic model of RABV-G. A single protomer of RABV-G is shown in cartoon representation. PHD is colored yellow, CD in blue, and FD in green, whereas the inter-domain linkers (L1−L5) are colored in dark gray. N- and C-termini are shown as blue and red spheres, respectively. The point mutation H270P is colored orange and shown in stick representation.
(E) Structure superimposition of our trimeric RABV-G with a previously reported monomeric RABV-G ectodomain structure obtained at pH 8.0. (RABV-Gecto, white cartoon, PDB: 6LGX) (Yang et al., 2020). When domains were aligned separately, the PHD and CD aligned more closely than the FD (calculated root-mean-square deviations 1.0-Å over 72 equiv C⍺ atoms for PHD, and 0.6-Å/128 C⍺ for CD, and 2.4-Å/88 C⍺ for FD). Differences in the L4 and L5 linkers between our trimeric RABV-G structure and the previous RABV-Gecto structure are highlighted in the inset.
For further information, see Figures S1–S3 and Tables S1 and S2.