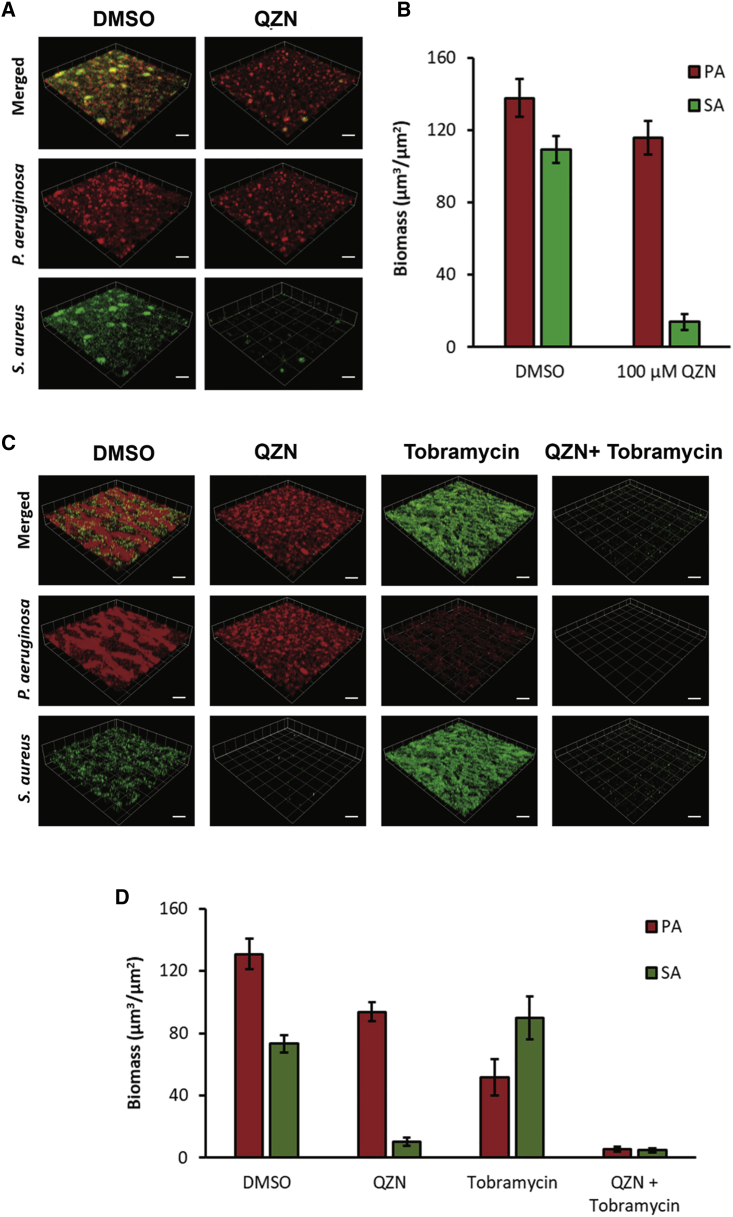
Figure 5.
Impact of 3-C3NH2-7Cl-C9-QZN 34 and tobramycin on P. aeruginosa and S. aureus mixed biofilms
(A and B) 3-C3NH2-7Cl-C9-QZN 34 confers partial protection of P. aeruginosa (PA) in a mixed-species biofilm with S. aureus (SA). Biofilms were allowed to form on glass after sequential inoculation with GFP-labeled S. aureus SH1000 (green) and mCherry labeled P. aeruginosa PAO1 (red) in a 10:1 ratio in RPMI 1640 containing either DMSO (vehicle control) or QZN 34 (100 μM) and incubated for 48 h.
(C and D) Combined effect of 3-C3NH2-7Cl-C9-QZN 34 and tobramycin on a mixed-species biofilm. The biofilm was allowed to form on glass after sequential inoculation with GFP-labeled S. aureus SH1000 (green) and mCherry labeled P. aeruginosa PAO1 (red) in a 10:1 ratio in RPMI 1640 containing either DMSO (vehicle control) or QZN 34 (100 μM) and incubated for 48 h. For some experiments, tobramycin (100 μg/mL) was also added, and the biofilms were cultured for a further 4 h.
(A and C) show 3D confocal microscope images. (B and D) show biomass quantification of the mixed-species biofilms after treatment. Scale bars, 50 μm. Data are means from 3 independent experiments ± SD.