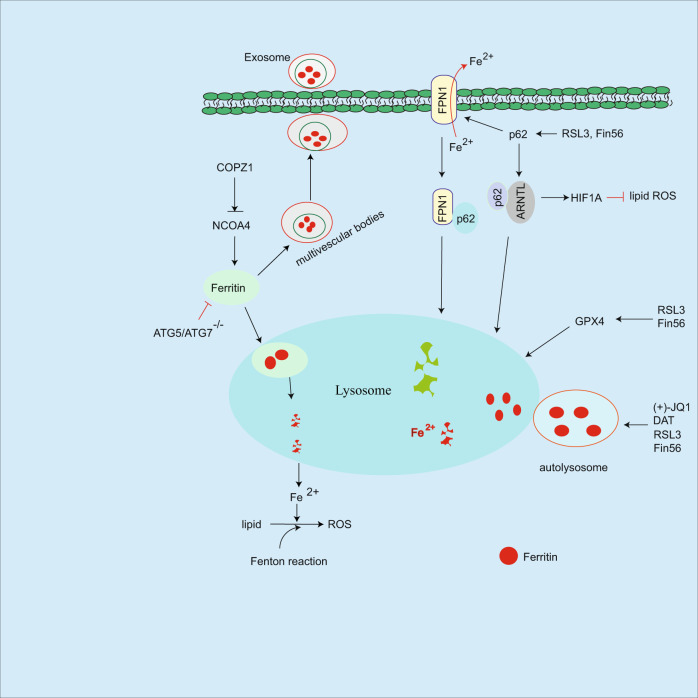
Fig. 3. Regulation of autophagy on ferroptosis.
NCOA4 induces ferritin autophagic degradation leading to the release of iron, which in turn facilitates ferroptosis, while COPZ1 inhibits NCOA4/ferritin pathway. Ferritin could be embedded into multivesicular bodies and traffic out of cells as exosome leading to reduced intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis resistance. In response to inducers, p62-mediated FPN1 or ARNTL autophagic degradation, which in turn promote sensitivity of ferroptosis. Although ferritinophagy is triggered in response to inducers including RSL3, Fin56, DAT etc, the mechanism is unclear.