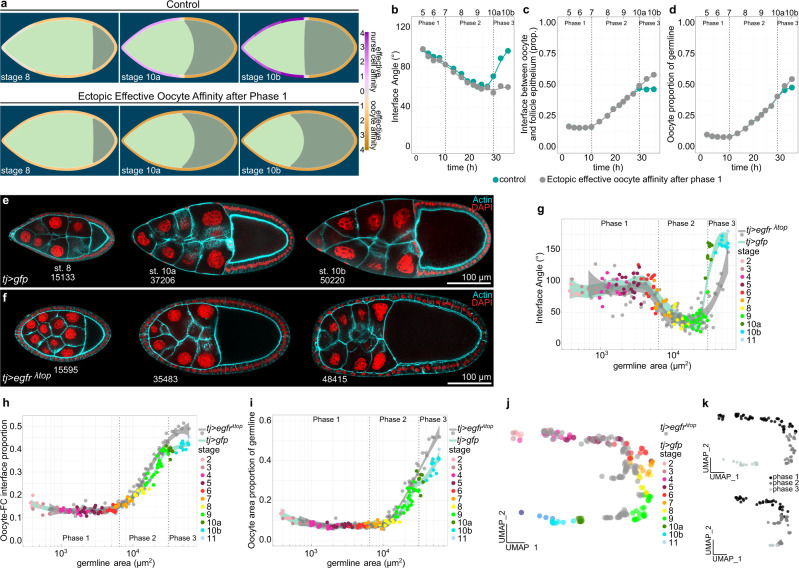
Fig. 9. Inhibition of AFC differentiation causes ectopic oocyte affinity and oocyte expansion during phase 3.
a Phase field model simulating germline cell behaviour as a function of their affinity for the follicle epithelium. wt affinity dynamics vs. ectopic effective oocyte affinity after phase 1 (simulating an Eya-negative follicle epithelium after phase 1). b–d Individual morphological parameters of the simulation as a function of time. b Interface Angle. c Proportion of the germline-FC interface made up by the oocyte. d Oocyte proportion of the germline. Phase boundaries were assigned to mid stage 7 and mid stage 10a. e Medial confocal sections of egg chambers expressing CD8-tom and gfp under the control of tj-GAL4 (tj > gfp, FC driver), stained for F-Actin and nuclei (DAPI). Numbers denote germline areas in µm2. f Medial confocal sections of egg chambers expressing CD8-tom and egfrλtop under the control of tj-GAL4 (tj > egfrλtop, FC driver), stained for F-Actin and nuclei (DAPI). Numbers denote germline areas in µm2. g–i Individual morphological parameters as a function of germline area for tj > gfp and tj> egfrλtop egg chambers. g Interface Angle. h Proportion of the germline-FC interface made up by the oocyte. i Oocyte proportion of the germline. Dotted lines mark germline sizes at the transition between two phases. Curves are LOESS fitted with a 95% CI area. n (tj > gfp: 119 ECs, tj > egfrλtop: 109 ECs). j UMAP comparing tj > gfp and tj > egfrλtop egg chamber morphogenesis. k UMAP of tj > gfp and tj > egfrλtop grouped into phase 1 (black, germline area<6500µm2), phase 2 (darkgrey, germline area >6500 µm2 & <31500 µm2), and phase 3 (lightgrey, germline area > 31500µm2). See Supplementary Table 7 for detailed statistical information. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.