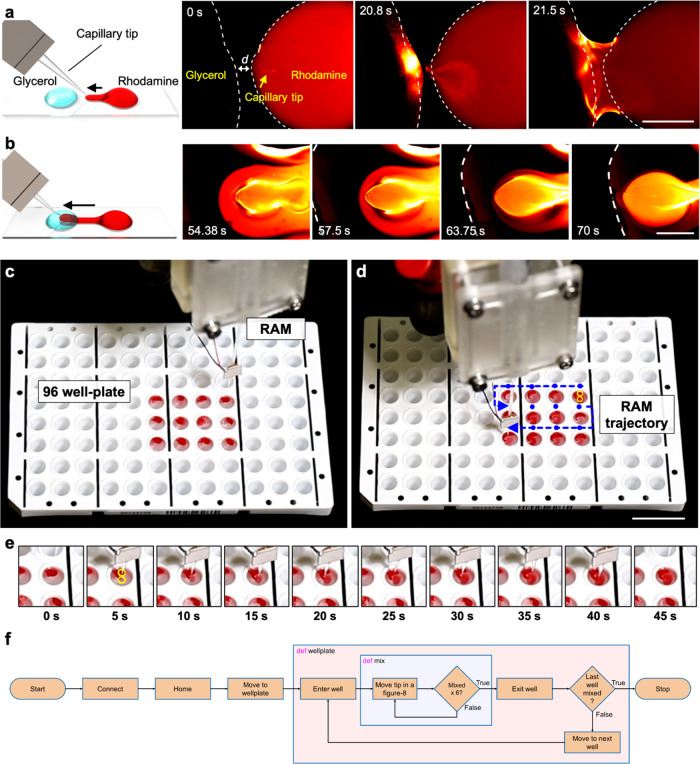
Fig. 7. Pre-programmed high-throughput mixing of viscous fluids in a 96-well plate using the RAEE.
a Conceptual schematic showing the merging of two droplets (left). Image sequences demonstrate the merging of glycerol (black) and rhodamine solution (red) droplets. Dotted white lines indicate droplet contours. Scale bar: 500 µm b Schematic showing the mobile mixing of rhodamine and glycerol droplets. MAEE was utilized to achieve mobile mixing of rhodamine solution in a glycerol droplet. Dotted white line indicates the contour of the glycerol droplet. c The RAEE system in the initial position above the plate, prior to mixing. d Device trajectory for the mixing process, indicated by blue dots and arrows. Movement that occurs while mixing inside a well is indicated by yellow lines (see Supplementary Movie 13). Scale bar: 20 mm. e Mixing procedure in a representative well, where the frame at 0 s indicates the unmixed state and that at 45 s indicates the mixed state. The yellow line indicates the path of the RAEE system inside the well while mixing (see Supplementary Movie 13). f The schematic illustrates the algorithm used by RAEE to achieve homogenous mixing in a 96-well plate.