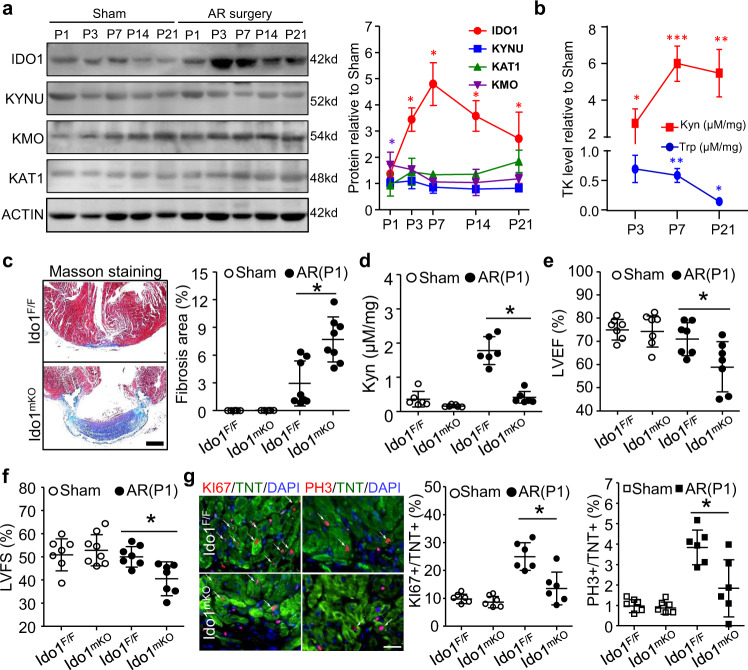
Fig. 1. IDO1-derived Kyn promotes neonatal heart regeneration.
a, b Postnatal 1 day (P1) wild-type mice underwent heart apical resection (AR) or Sham surgery. The regenerating hearts were collected at P3, P7, P14, and P21. a Western blot assay and quantification showing the expression profiles of tryptophan-kynurenine (Trp-Kyn, TK) metabolic mediators during heart regeneration (n = 6/stage). b Kyn and Trp levels measured by HPLC. *P < 0.05 vs. the Sham group at the indicated times (n = 6/stage). c–f Ido1 F/F (Ido1 Flox/Flox) and Ido1 mKO (Tnt Cre; Ido1 Flox/Flox) mice underwent AR or Sham surgery at P1 and heart was collected at P21 for HPLC, Masson staining and echocardiography assay. c Representative images and quantitation of fibrosis area by Masson staining (n = 6 for Sham Ido1 F/F and Sham Ido1 mKO; n = 8 for AP Ido1 F/F and AP Ido1 mKO). Bar = 500 µm. d Cardiac Kyn level measured by HPLC assay (n = 6/group). e, f left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF, e) and fractional shortening (LVFS, f) analyzed by echocardiography (n = 7/group). g Cardiomyocyte (CM) proliferation assessed by co-staining of KI67 or PH3 with Troponin T (TNT) at P7 (n = 6/group). Bar = 20 µm. Data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test in (a, b), one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test in c (P = 0.0002), d (P < 0.0001), e (P = 0.178), f (P = 0.042), and g (P = 0.0005 for KI67 and P = 0.0029 for PH3).