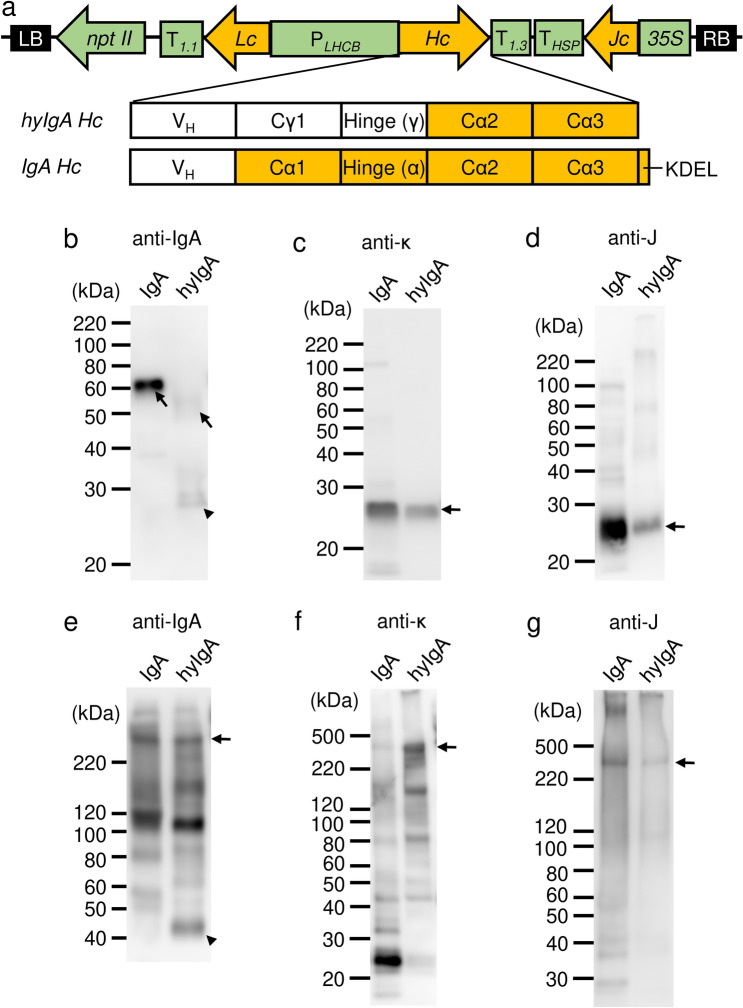
Figure 1.
Production of IgA plantibody specific for Stx1B in a plant expression system. (a) Schematic diagram of the transfer-DNA (T-DNA) region of the Stx1B-specific dimeric IgA expression vector (pRI201/dimeric IgA). PLHCB, light-harvesting complex II (LHCB) promoter; T1.1 and T1.3, LHCB terminators; Hc, IgA heavy chain gene; Lc, IgA light chain gene; Jc, immunoglobulin joining chain gene; 35S, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; THSP, terminator of Arabidopsis heat shock protein 18.2 gene; nptII, neomycin phosphotransferase II gene; LB, left border of T-DNA region; RB, right border of T-DNA region. Immunoglobulin domain organizations of the heavy chain inserts for the hyIgA and IgA are shown in parallel. VH, variable region; Cγ, heavy chain constant regions from IgG1; Cα, those from IgA; Hinge (γ or α), hinge region from IgG1 or IgA; KDEL, the endoplasmic reticulum retention signal peptide. (b–g) Immunoblot analysis of leaf extracts of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Leaf proteins (b,c,e,f, 10 ng/lane as IgA; d,g, 30 ng/lane as IgA) were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing (b–d: 12% gel) and non-reducing (e–g: 4–15% gradient gel) conditions, and then blotted onto PVDF membranes. Each immunoglobulin chain was detected with anti-IgA heavy chain (b,e), anti-κ light chain (c,f), and anti-J chain (d,g) antibodies, respectively. Arrows indicate the intact immunoglobulin chains and arrowheads indicate the incomplete IgA heavy chains. Leaf extracts of Stx1B-specific IgA transgenic A. thaliana (IgA) or hyIgA transgenic A. thaliana (hyIgA) were analyzed.