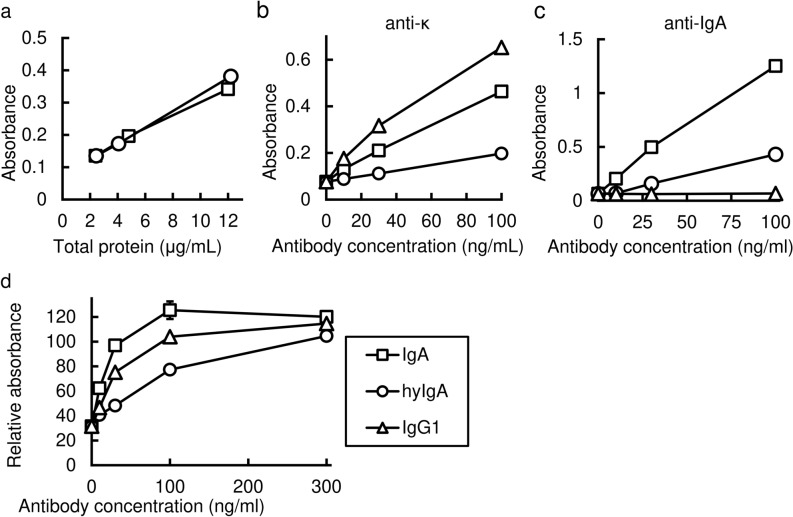
Figure 2.
Antigen-recognition and neutralization activity of the Stx1B-specific IgA plantibody in vitro. (a) Detection of assembled IgA by sandwich ELISA. Signals for IgA carrying both heavy and light chains (ordinate) were plotted against the protein concentrations (abscissa) in the leaf extracts of transgenic plants that express IgA (squares) or hyIgA (circles). Data are expressed as means for triplicate determinations, and SDs were shorter than each symbol. (b,c) Dose-dependent binding of IgA and an IgG1 mAb antibody to the immobilized Stx1B in response to antibody concentration (abscissa). Signals for the bound antibodies were detected using anti-κ light chain antibodies (ordinate) (b) or anti-IgA heavy chain antibodies (c). Samples from IgA (squares) or hyIgA (circles) transgenic plants, or hybridoma-derived mouse IgG1 mAb (triangles) were analyzed. Data are expressed as means of duplicate determinations, and the ranges were shorter than each symbol. (d) Neutralization of Stx1 cytotoxicity by IgA plantibodies and the IgG1 mAb in vitro. One hundred pg/mL of Stx1 was treated with various concentrations of Stx1B-specific antibodies (abscissa) for 1 h. Vero cells were incubated with an Stx1/antibody mixture for 45 h, and then live cells were quantitated by the WST-8 assay. The ordinate indicates the relative OD450 for each culture compared with the control condition (no toxin exposure). The indicated amount of antibody (abscissa) present in the leaf extract of IgA- (squares) or hyIgA- (circles) transgenic plants, or in the IgG1-producing hybridoma culture supernatants (triangles) was added to each culture. Data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate cell cultures. The results are representative of three experiments.