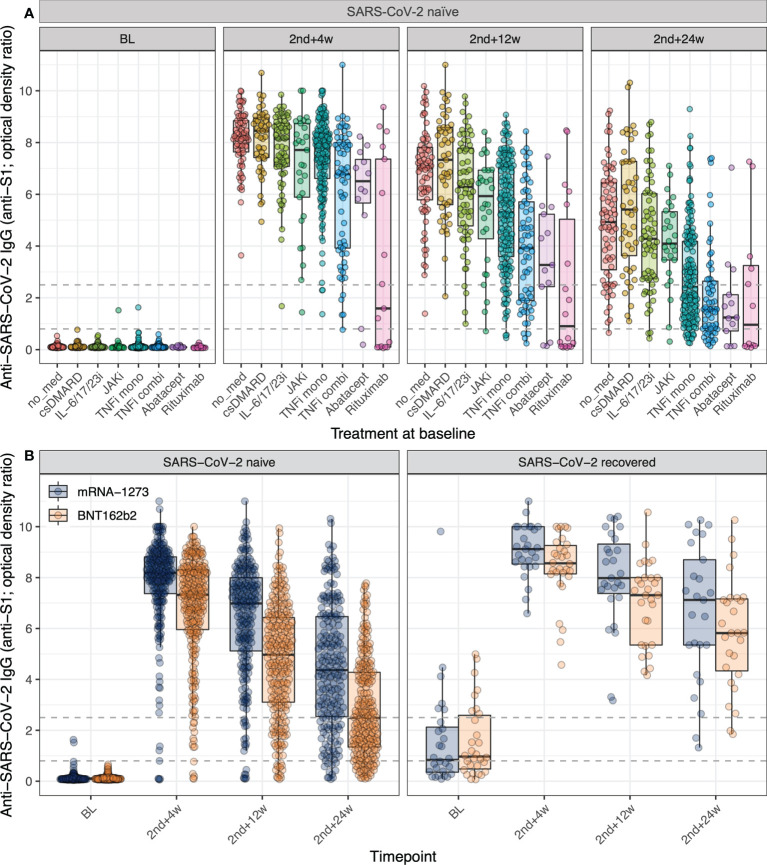
Figure 1.
Impact of treatment for IRD and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine on anti-S1 antibody levels. (A) The variation over time of anti-S1 antibodies post mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in adult SARS-CoV-2 naïve IRD patients disaggregated by treatment group at baseline. No med = currently on no medication; csDMARD = conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in mono or combination therapy with GC (glucocorticoids); IL-6/17/23i = interleukin 6/17/23 inhibitors in mono or combination therapy with csDMARD/csDMARD & GC; JAKi = janus kinase inhibitors in mono or combination therapy with csDMARD/csDMARD & GC; TNFi mono = tumor necrosis factor inhibitor as monotherapy, TNFi combi = TNFi in combination therapy with csDMARD/GC/csDMARD & GC; Abatacept in mono or combination therapy with csDMARD/csDMARD & GC; Rituximab in mono or combination therapy with csDMARD/csDMARD & GC. The following treatment groups with five or fewer participants are not shown here: GC monotherapy and PDE4i (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) in mono or combination therapy with csDMARD. (B) The variation over time of anti-S1 antibodies post mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in adult IRD patients disaggregated by vaccine and evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection. For both panels: The dashed lines indicate the assay thresholds (see Methods). Individual points are overlaid on boxplots, with whiskers extending to 1.5*IQR. BL = baseline (day of 1st vaccine dose, before vaccination), 2nd+4w/12w/24w = 4/12/24 weeks post 2nd vaccine dose. For the full, adjusted model outcomes, see Table 2 .