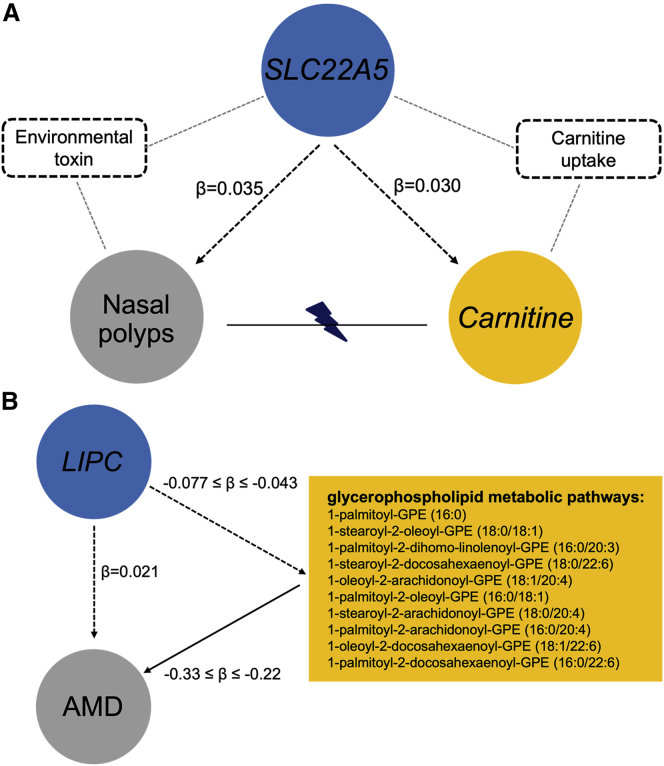
Figure 6.
Genetic causal pathways
(A) Two potentially distinct metabolic pathways mediate the effect of SLC22A5 expression on the risk of nasal polyps and the level of plasma carnitine level; (B) glycerophospholipid metabolic pathways mediate the effect of LIPC expression on the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Blue circles represent the shared putative causal genes between metabolites and diseases. Yellow circles and rectangles represent metabolites. Gray circles represent disease outcomes. Dashed rectangles and gray dashed lines depict potential environmental risk factors that mediate the effect of SLC22A5 expression levels on carnitine levels and nasal polyps risk. The black dashed arrows depict the estimated effects of gene expression on metabolite levels or disease risk in PTWASs. The black solid arrow denotes the putative causal effects of the ten glycerophospholipids on the risk of AMD, which are estimated in the Mendelian randomization analysis. The flash symbol indicates that Mendelian randomization was unable to detect significant causal relationship between nasal polyps risk and plasma carnitine level.