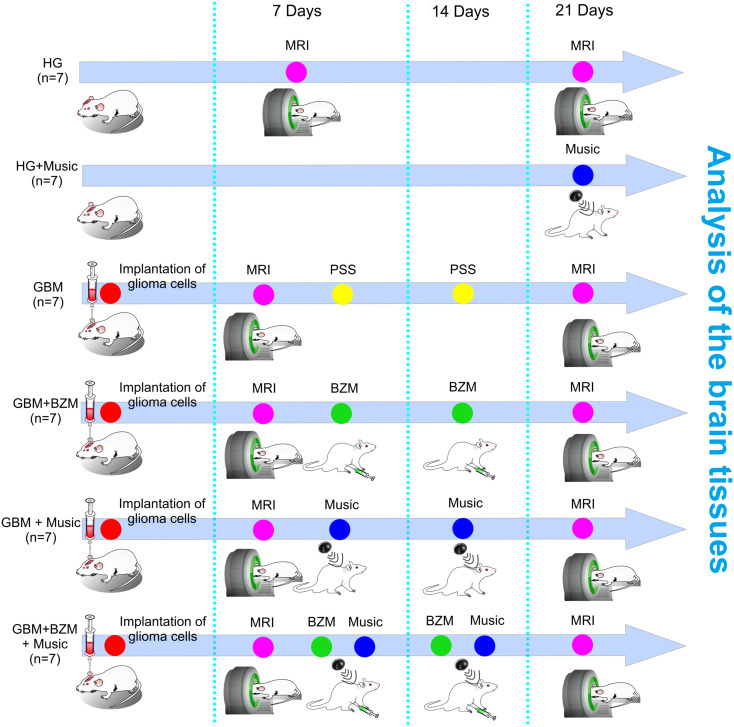
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the design of the experiments. The rats were divided into six groups: (1) GBM, the group included rats with GBM and received intraperitoneal injection of PSS; (2) GBM+Music, the group included rats with GBM and the music-induced BBB opening; (3) GBM+BZM, the group included rats with GBM and received intraperitoneal injection of BZM; (4) GBM+BZM+Music, the group included rats with GBM treated by music and received intraperitoneal injection of BZM; (5) HG, the group included healthy sham rats with the injection of PSS in the same volume and in the same area of the brain, which was selected for the injection of glioma cells; (6) HG + Music, the group included the healthy rats with the music-induced BBB opening; n=7 in each group. The PSS and BZM (10 mg/kg) intraperitoneal injection were performed 7 days and 14 days after the implantation of glioma cells into the rat brain. The MRI analysis of GBM growth and the tumor volume was performed 7 and 21 days post tumor cell implantation. The rats from the GBM+Music and the GBM+BZM+Music groups listened music on 7 and 14 days of tumor growth; rats from the HG group listened music on 21 day of observation. GBM, glioblastoma; BZM, bevacizumab; HG, healthy group; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PSS, physiological saline solution.