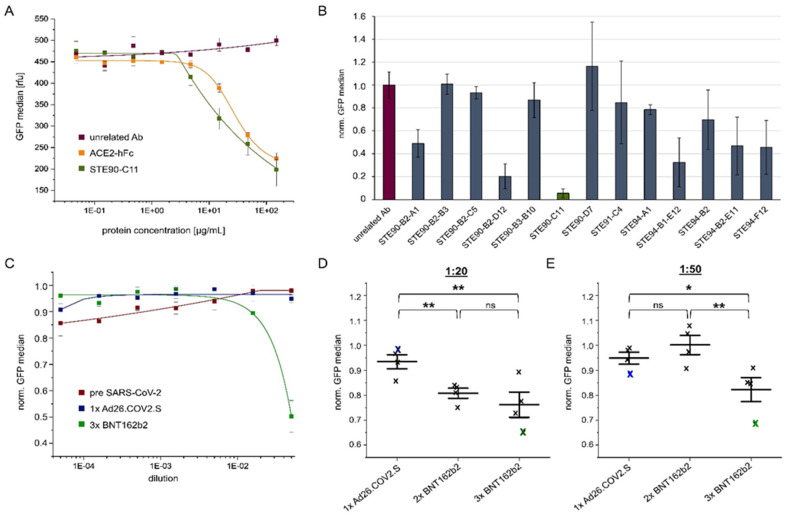
Figure 5.
Analysis of anti-spike antibody candidates, ACE2-hFc, or sera by cellular VLP binding assay to measure their respective inhibition potential. (A) Absolute GFP values when unrelated antibody (Ab), ACE2-hFc, or STE90-C11 (IgG) were applied for inhibition of the VLP binding to ACE2 positive cells at the indicated concentrations. (B) Obtained inhibition of VLP binding using different antibody candidates at a concentration of 150 µg/mL. Bars represent the normalized binding activity by setting the VLP binding without antibody to 1 and binding to ACE2 negative cells to 0. (C) Inhibition of VLP cell binding by human sera from, respectively, one pre-SARS-CoV-2 donor or individuals vaccinated with 1× Ad26.COV2.S or 3× BNT162b2. Values represent the binding activity normalized by setting the signal of VLP binding to ACE2 positive cells without sera to 1 and binding to ACE2 negative cells to 0. (D) VLP cell binding inhibition by sera from 1× Ad26.COV2.S, 2× BNT162b2, or 3× BNT162b2 vaccinated donors at a dilution of 1:20. The blue or green crosses identify the sera used in (C). (E) Inhibition of the same sera used in B at a dilution of 1:50. The blue or green crosses identify the sera used in (C). All experiments were performed in triplicates using one batch of VLP but three independent batches of ACE2 (or mock) transfected Expi293F cells. The standard deviation is indicated by error bars. Significances were determined by two-sided t-Test (* = 90%, ** = 95%).