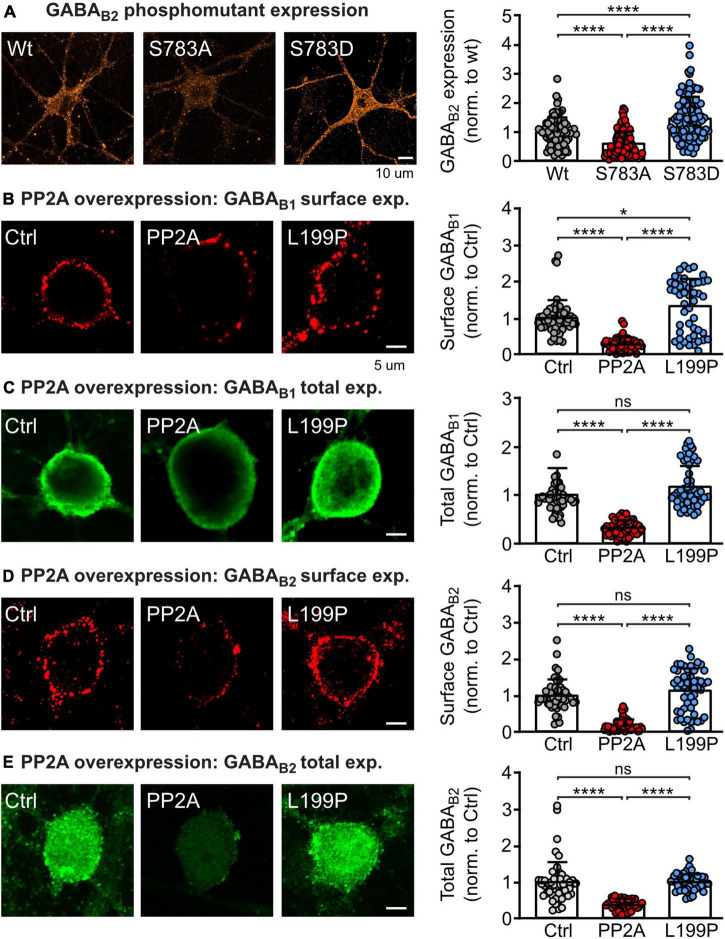
FIGURE 1.
PP2A regulates GABAB receptor expression. (A) Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of GABAB2(S783) affects expression of GABAB receptors. Neurons were transfected either with wild type HA-tagged GABAB2, a HA-tagged GABAB2 mutant with inactivated S783 phosphorylation site 783 (S783A) or with a mutation mimicking phosphorylation of this site (S783D) along with wild type GABAB1. Expression of HA-tagged GABAB receptors was determined after 2 days by staining with antibodies directed against the HA-tag. Left: Representative images of total GABAB receptor expression (scale bar: 10 μm). Right: Quantification of GABAB2 staining. Expression levels were normalized to the control (wild type HA-GABAB2). The data represent the mean ± SD of 87–144 neurons from three independent. Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA with Games Howell’s multiple comparison test (****p < 0.0001). (B–E) Overexpression of the catalytic subunit of PP2A (PP2A-C) downregulates total and cell surface expression of GABAB receptors in neurons. Neurons were transfected with EGFP and either PP2A-C or an inactive mutant of PP2A-C (L199P). Cell surface and total endogenous GABAB1 (B,C) and endogenous GABAB2 (D,E) was determined after 2 days via staining with GABAB1 and GABAB2 antibodies. Left: Representative images (scale bar: 5 μm). Right: Quantification of GABAB receptor staining. Signals were normalized to the control (only transfected with EGFP). The data represent the mean ± SD of 87–144 neurons from three independent. Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA with Games Howell’s multiple comparison test (ns, p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001).