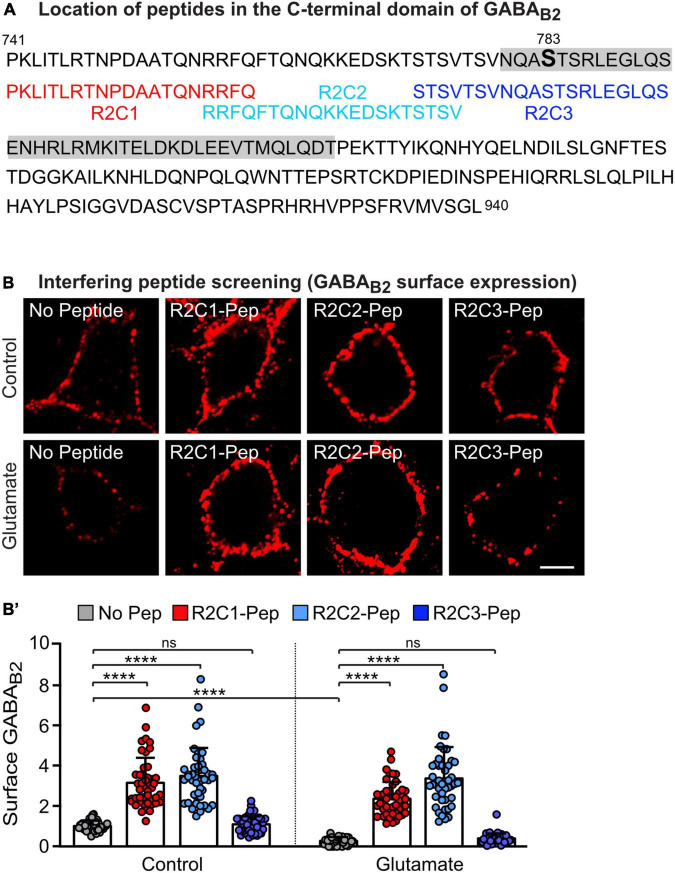
FIGURE 2.
Screening for a peptide sequence present in the C-terminal domain of GABAB2 that blocks glutamate-induced downregulation of GABAB receptors. (A) Sequence of the C-terminal domain of GABAB2 with the coiled-coil domain indicated in gray and the overlapping peptides R2C1, R2C2 and R2C3 used in (B) shown below. (B,B’) Peptides R2C1 and R2C2 increased expression of GABAB receptors and restored glutamate-induced downregulated receptor cell surface levels. Cultures were stressed for 60 min with glutamate (50 μM) and immediately thereafter treated for 16 h with the peptides indicated in (A). Neurons were then tested for cell surface expression of endogenous GABAB receptors using antibodies directed against the N-terminus of GABAB2. (B) Representative images of GABAB2 cell surface staining (scale bar: 5 μm). (B’) Quantification of the fluorescence intensities. The data were normalized to cultures not treated with glutamate and peptides and represent the mean ± SD of 45 neurons derived from three independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (ns, p > 0.05, ****p < 0.0001.