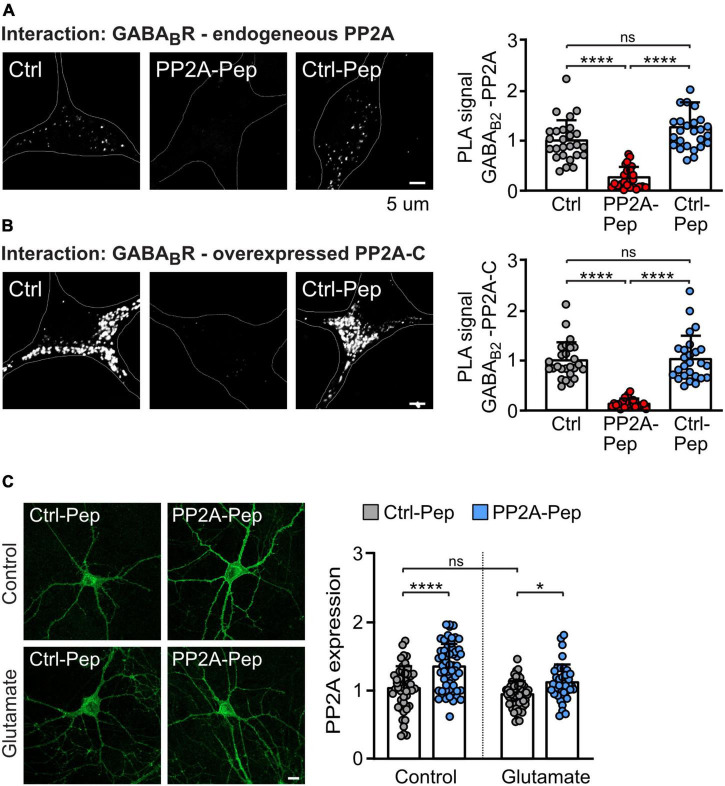
FIGURE 3.
PP2A-Pep inhibits the interaction of GABAB receptors with PP2A and does not downregulate PP2A expression. (A,B) PP2A-Pep prevents the PP2A/GABAB receptor interaction. (A) The interaction of endogenous PP2A with endogenous total (cell surface and intracellular) GABAB receptors in the presence or absence of PP2A-Pep (10 μM) was analyzed by in situ PLA using antibodies directed against PP2A and GABAB2. (B) The interaction of GABAB receptors and the overexpressed catalytic subunit of PP2A (PP2A-C) in the presence or absence of PP2A or Ctrl-Pep was analyzed by in situ PLA. Neurons were co-transfected with EGFP for identification of PP2A-C overexpressing neurons. Neurons transfected only with EGFP and not treated with peptides served as controls. Left: representative images (white dots represent interactions, scale bar: 5 μm). Right: quantification of the in situ PLA signals. The data were normalized to control cultures not treated with peptides and represent the mean ± SD of 26 neurons derived from three independent experiments. Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA with Games Howell’s multiple comparison test (ns, p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, ****p > 0.0001). (C) PP2A-Pep does not downregulate PP2A expression. Glutamate-stressed and unstressed neurons were treated with PP2A-Pep (10 μM) and analyzed for PP2A expression. Left: representative images (scale bar: 10 μm). Right: quantification of the immunofluorescence. The data were normalized to control cultures not treated with glutamate and peptide and represent the mean ± SD of 38–60 neurons derived from three independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (ns, p > 0.05; *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001).