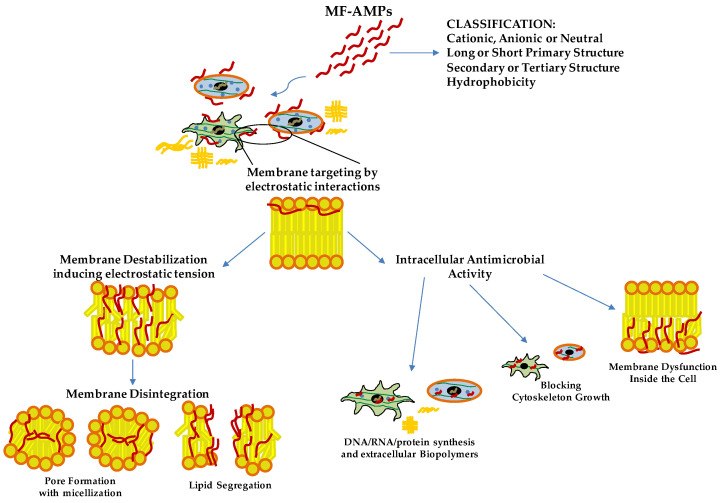
Figure 1.
Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Action ofMultifunctional Antimicrobial Peptides (MF-AMPs). Based on their biochemical characteristics, MF-AMPs can interact with the membrane lipids, inducing the pathogens’ instability and rigidity of the cell membrane. Upon reaching the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values, they cause pore formation and cell lysis. Some MF-AMPs exert a cell-penetrating peptides-like function. They can penetrate the membrane, blocking pathogens’ growth by internal membrane dysfunction, cytoskeleton interaction and interference of biomolecules production. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA); ribonucleic acid (RNA).