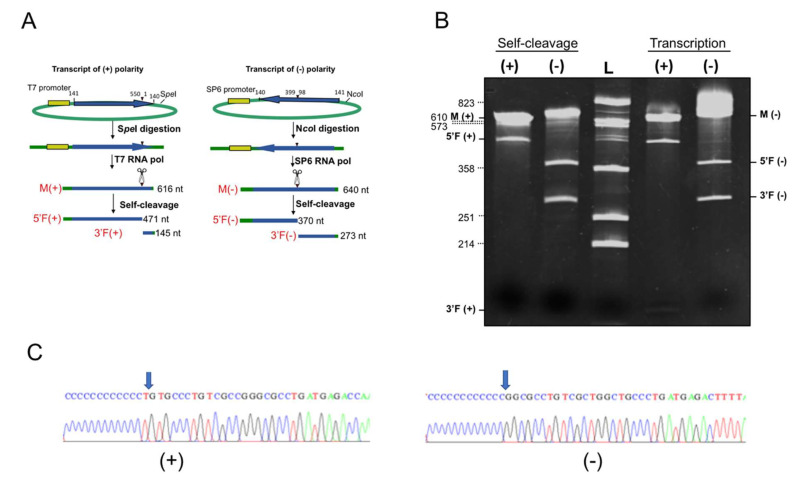
Figure 5.
(A) Schematic representation of the plasmids and the RNA products generated by in vitro transcription. Plasmids containing the monomeric cDNA sequence of CtaHVd-LR1_3 in opposite orientations were linearized and transcribed to produce monomeric RNAs (M) of (+) and (−) polarity strands and the respective 5′ (5′F) and 3′ (3′F) fragments (left and right, respectively) derived from the HHRz self-cleaving activity. Plasmid sequences are depicted in green, while in yellow and blue are the polymerase promoter and CtaHVd-LR1 sequences, respectively. The scissors and arrowhead mark the position of the self-cleavage sites. The expected size of each fragment is reported on the right. (B) Analysis by 5% PAGE under denaturing conditions of the in vitro transcription (left) and self-cleavage reaction in the absence of any protein (right) of the plasmids containing (+) or (−) monomeric CtaHVd-LR1_3 cDNA. L, RNA ladder with sizes indicated on the left; see panel A for the abbreviations M, 3′F and 5′F. (C) Determination of self-cleavage site by 5′ RACE of 3′F fragment. Sequencing electropherograms of 5′ RACE products of the (+) and (−) 3′F fragments are shown on the left and right, respectively, with the 5′ terminal nucleotide (G) indicated by the arrow. The extra T observed at the terminal end of the (+) 3′F fragment cDNA (left) correspond to a non-template nucleotide that has likely been added by the reverse transcriptase during the cDNA synthesis [50].