Figure 3:
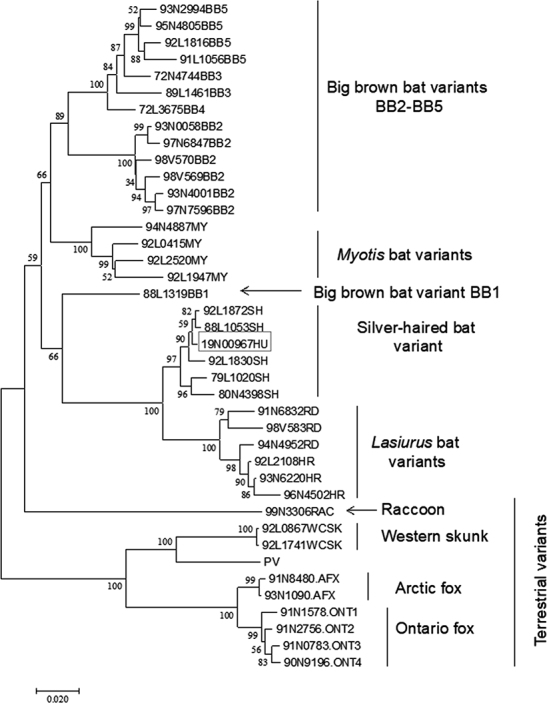
Phylogenetic analysis of the RABV sample (19N00967HU) from the BC human rabies case compared with representative viruses from known RABV variants circulating in Canada
Numbers at all nodes of the tree indicate their respective bootstrap values expressed as a percentage, and branches represent genetic distances according to the scale shown at bottom. Major clades are identified to the right of the tree. RNA extracted from saliva using TRIzol reagent (ThermoFisher) was used as template to amplify the complete RABV N gene as two overlapping nested RT-PCRs according to previously described protocols (1). The amplicons were purified using a GeneJet PCR purification kit (ThermoFisher), sequenced using internal primers with a BDT v3.1 sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems), and run on a 3500xl Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems). Reads were assembled using the SeqManPro software of the DNASTAR Lasergene v 14 package. MEGA v7 was used to align the assembled sequence with a database of N gene sequences representative of the RABV variants that circulate within Canada and to generate the phylogenetic tree using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates.
RABV = Rabies virus; BC = British Columbia
