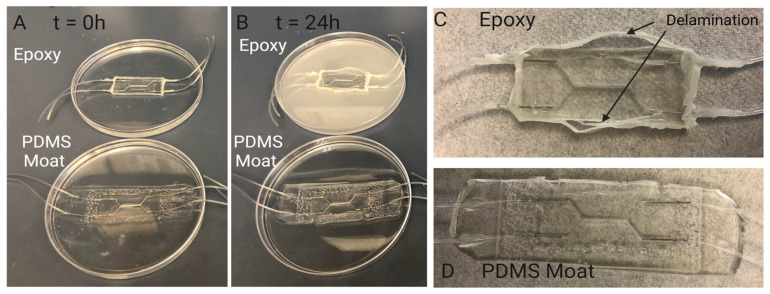
Figure 8.
Investigating PDMS device sealing method. Sealing with PDMS moat prevents delamination during cell culture period. Comparison of degradation of sealing methods over 24 h: (A) Samples are submerged in 70% ethanol to accelerate the degradation seen in other aqueous liquids such as cell culture media. When initially placed in ethanol there are no visual signs of degradation in chips sealed with epoxy and chips sealed with a PDMS moat. (B) After 24 h, the ethanol in which the chip seal with epoxy is submerged exhibits a discoloration indicating a degradation of the epoxy. The chip sealed with PDMS moat shows no signs of discoloration or breakdown. Visual inspection of chips sealed with (C) epoxy and (D) PDMS moat (D) after 24hrs of submersion in ethanol. Over 24 h of submersion, the Epoxy-PDMS interface begins to delaminate and separation between the two layers can be seen macroscopically. This separation results in limited support for preventing leakage in chips when higher pressures are experienced within the device.